Abstract
Identification of bioactive compounds directly from complex herbal extracts is a key issue in the study of Chinese herbs. The present study describes the establishment and application of a sensitive, efficient, and convenient method based on surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensors for screening active ingredients targeting tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1 (TNF-R1) from Chinese herbs. Concentration-adjusted herbal extracts were subjected to SPR binding assay, and a remarkable response signal was observed in Rheum officinale extract. Then, the TNF-R1-bound ingredients were recovered, enriched, and analyzed by UPLC-QTOF/MS. As a result, physcion-8-O-β-d-monoglucoside (PMG) was identified as a bioactive compound, and the affinity constant of PMG to TNF-R1 was determined by SPR affinity analysis (K D = 376 nM). Pharmacological assays revealed that PMG inhibited TNF-α-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in L929 cells via TNF-R1. Although PMG was a trace component in the chemical constituents of the R. officinale extract, it had considerable anti-inflammatory activities. It was found for the first time that PMG was a ligand for TNF receptor from herbal medicines. The proposed SPR-based screening method may prove to be an effective solution to analyzing bioactive components of Chinese herbs and other complex drug systems.

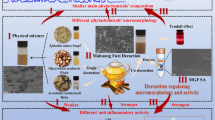
Scheme of the method based on SPR biosensor for screening and recovering active ingredients from complex herbal extracts and UPLC-MS for identifying them. Scheme of the method based on SPR biosensor for screening and recovering active ingredients from complex herbal extracts and UPLC-MS for identifying them





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Acetic acid
- FA:
-
Formic acid
- PMG:
-
Physcion-8-O-β-d-monoglucoside
- SPR:
-
Surface plasmon resonance
- TFA:
-
Trifluoro acid
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
References
Liu S, Yi L-Z, Liang Y-Z. Traditional Chinese medicine and separation science. J Sep Sci. 2008;31(11):2113–37.
Chen X, Cao Y, Lv D, Zhu Z, Zhang J, Chai Y. Comprehensive two-dimensional HepG2/cell membrane chromatography/monolithic column/time-of-flight mass spectrometry system for screening anti-tumor components from herbal medicines. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1242:67–74.
Harvey AL. Natural products in drug discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2008;13(19–20):894–901.
Zhu Y, Zhang Z, Zhang M, Mais DE, Wang M-W. High throughput screening for bioactive components from traditional Chinese medicine. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2010;13(10):837–48.
Wang S, Sun M, Zhang Y, Du H, He L. A new A 431/cell membrane chromatography and online high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry method for screening epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists from Radix sophorae flavescentis. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217(32):5246–52.
Chen X, Cao Y, Zhang H, Zhu Z, Liu M, Liu H, et al. Comparative normal/failing rat myocardium cell membrane chromatographic analysis system for screening specific components that counteract doxorubicin-induced heart failure from Acontium carmichaeli. Anal Chem. 2014;86(10):4748–57.
Cao Y, Chen X-F, Lü D-Y, Dong X, Zhang G-Q, Chai Y-F. Using cell membrane chromatography and HPLC-TOF/MS method for in vivo study of active components from roots of Aconitum carmichaeli. J Pharm Anal. 2011;1(2):125–34.
Wang X, Sun H, Zhang A, Jiao G, Sun W, Yuan Y. Pharmacokinetics screening for multi-components absorbed in the rat plasma after oral administration traditional Chinese medicine formula Yin-Chen-Hao-Tang by ultra performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with pattern recognition methods. Analyst. 2011;136(23):5068–76.
Yang H, Chen J, Tang S, Li Z, Zhen Y, Huang L, et al. New drug R&D of traditional Chinese medicine: role of data mining approaches. J Biol Syst. 2009;17(03):329–47.
Liang X, Li H, Li S. A novel network pharmacology approach to analyse traditional herbal formulae: the Liu-Wei-Di-Huang pill as a case study. Mol BioSyst. 2014;10(5):1014–22.
Campbell CT, Kim G. SPR microscopy and its applications to high-throughput analyses of biomolecular binding events and their kinetics. Biomaterials. 2007;28(15):2380–92.
Homola J. Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2003;377(3):528–39.
Phillips KS, Cheng Q. Recent advances in surface plasmon resonance based techniques for bioanalysis. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;387(5):1831–40.
Homola J. Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem Rev. 2008;108(2):462–93.
Peng M, Zhang Y, Shi S, Peng S. Simultaneous ligand fishing and identification of human serum albumin binders from Eucommia ulmoides bark using surface plasmon resonance-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 2013;940:86–93.
Zhang Y, Shi S, Guo J, You Q, Feng D. On-line surface plasmon resonance-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of human serum albumin binders from Radix Astragali. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1293:92–9.
Marchesini GR, Buijs J, Haasnoot W, Hooijerink D, Jansson O, Nielen MWF. Nanoscale affinity chip interface for coupling inhibition SPR immunosensor screening with nano-LC TOF MS. Anal Chem. 2008;80(4):1159–68.
Stigter ECA, de Jong GJ, van Bennekom WP. Development of an on-line SPR-digestion-nanoLC-MS/MS system for the quantification and identification of interferon-γ in plasma. Biosens Bioelectron. 2009;24(7):2184–90.
Chu X, Wei M, Yang X, Cao Q, **e X, Guan M, et al. Effects of an anthraquinone derivative from Rheum officinale Baill, emodin, on airway responses in a murine model of asthma. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012;50(7):2368–75.
Wang X, Jia W, Zhao A, Wang X. Anti-influenza agents from plants and traditional Chinese medicine. Phytother Res. 2006;20(5):335–41.
Shin EM, Zhou HY, Guo LY, Kim JA, Lee SH, Merfort I, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of glycyrol isolated from Glycyrrhiza uralensis in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008;8(11):1524–32.
Lee D-Y, Noh H-J, Choi J, Lee K-H, Lee M-H, Lee J-H, et al. Anti-inflammatory cycloartane-type saponins of Astragalus membranaceus. Molecules. 2013;18(4):3725–32.
Wang B-Q. Salvia miltiorrhiza: chemical and pharmacological review of a medicinal plant. J Med Plants Res. 2010;4(25):2813–20.
Committee CP. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Bei**g: Chinese Medical Science and Technology Press; 2015.
Bradley JR. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J Pathol. 2008;214(2):149–60.
Shang X, Yuan Z. Determination of six components in Rhubarb by cyclodextrin-modified micellar electrokinetic chromatography using a mixed micellar system of sodium cholate and sodium taurocholate. Anal Chim Acta. 2002;456(2):183–8.
Gong YX, Li SP, Wang YT, Li P, Yang FQ. Simultaneous determination of anthraquinones in Rhubarb by pressurized liquid extraction and capillary zone electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2005;26(9):1778–82.
Guo X. Surface plasmon resonance based biosensor technique: a review. J Biophotonics. 2012;5(7):483–501.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81202496 and 81273472) and grants from the Second Military Medical University (No. 2011QN04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Yan Cao, Ying-hua Li and Di-ya Lv contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Y., Li, Yh., Lv, Dy. et al. Identification of a ligand for tumor necrosis factor receptor from Chinese herbs by combination of surface plasmon resonance biosensor and UPLC-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 5359–5367 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9633-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9633-6