Abstract
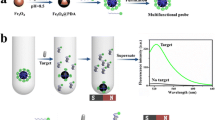
A double-receptor sandwich method for the fluorescence determination of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is proposed in this paper. The solid phase receptor on the surface of glass slides is a molecularly imprinted membrane (MIM) containing an artificial nanocavity. It is constructed by a molecular imprinting technique using adenosine monophosphate (AMP) as a template molecule. The labeled receptor is a uranyl–salophen complex containing a fluorescent group or uranyl–salophen–fluorescein (USF). It is synthesized with salophen, 5-aminofluorescein, and uranyl. In a procedure of determining ATP, ATP in sample solution is first adsorbed on the surface of the glass slide through the combination of the AMP group in ATP with the nanocavity in MIM. Then, the adsorbed ATP binds USF through the coordination reaction of the phosphate group in ATP with uranyl in USF to form a sandwich-type structure of MIM-ATP-USF. The amount of ATP is detected through the fluorescence determination of USF bound on the slide. Under optimal conditions, the linear range for the determination of ATP is 0.3 to 4.8 nmol/mL with a detection limit of 0.041 nmol/mL. The proposed method has been successfully employed for the determination of ATP in real samples with the recoveries of 98.5 to 102.5 %.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pérez-Ruiz T, Martínez-Lozano C, Tomás V, Martín J (2003) Determination of ATP via the photochemical generation of hydrogen peroxide using flow injection luminol chemiluminescence detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 377:189–194
Kiesslich T, Oberdanner CB, Krammer B, Plaetzer K (2003) Fast and reliable determination of intracellular ATP from cells cultured in 96-well microplates. J Biochem Biophys Method 57:247–251
Compagnone D, Guilbault GG (1997) Glucose oxidase/hexokinase electrode for the determination of ATP. Anal Chim Acta 340:109–113
Stratford MRL, Dennis MF (1994) Determination of adenine nucleotides by fluorescence detection using high-performance liquid chromatography and post-column derivatisation with chloroacetaldehyde. J Chromatogr B 662:15–20
Li W, Nie Z, Xu X, Shen Q, Deng C, Chen J, Yao S (2009) A sensitive, label free electrochemical aptasensor for ATP detection. Talanta 78:954–958
Wang J, Jiang Y, Zhou C, Fang X (2005) Aptamer-based ATP assay using a luminescent light switching complex. Anal Chem 77:3542–3546
Zhang S, Yan Y, Bi S (2009) Design of molecular beacons as signaling probes for adenosine triphosphate detection in cancer cells based on chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer. Anal Chem 81:8695–8701
Zuo X, Song S, Zhang J, Pan D, Wang L, Fan C (2007) A target-responsive electrochemical aptamer switch (TREAS) for reagentless detection of nanomolar ATP. J Am Chem Soc 129:1042–1043
Futakawa S, Kitazume S, Oka R, Ogawa K, Hagiwara Y, Kinoshita A, Miyashita K, Hashimoto Y (2009) Development of sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay systems for plasma β-galactoside α2,6-sialyltransferase, a possible hepatic disease biomarker. Anal Chim Acta 631:116–120
Wei Q, Lee M, Yu X, Lee EK, Seong GH, Choo J, Cho YW (2006) Development of an open sandwich fluoroimmunoassay based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Anal Biochem 358:31–37
Turiel E, Martin-Esteban A (2009) Molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase microextraction. J Sep Sci 32:3278–3284
Ou J, Li X, Feng S, Dong J, Dong X, Kong L, Ye M, Zou H (2007) Preparation and evaluation of a molecularly imprinted polymer derivatized silica monolithic column for capillary electrochromatography and capillary liquid chromatography. Anal Chem 79:639–646
Zhang Z, Yang X, Zhang H, Zhang M, Luo L, Hu Y, Yao S (2011) Novel molecularly imprinted polymers based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes with binary functional monomer for the solid-phase extraction of erythromycin from chicken muscle. J Chromatogr B 879:1617–1624
Zheng Y, Liu Y, Guo H, He L, Fang B, Zeng Z (2011) Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for determination of tilmicosin in feed using high performance liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 690:269–274
Plewa A, Yusa S-I, Szuwarzyński M, Szczubiałka K, Morishima Y, Nowakowska M (2012) Molecularly imprinted hybrid adsorbents for adenine and adenosine-5′-triphosphate. J Med Chem 55:8712–8720
Haginaka J, Tabo H, Matsunaga H (2012) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers for organophosphates and their application to the recognition of organophosphorus compounds and phosphopeptides. Anal Chim Acta 748:1–8
Matsui J, Nagano J, Miyoshi D, Tamaki K, Sugimoto N (2009) An approach to peptide-based ATP receptors by a combination of random selection, rational design, and molecular imprinting. Biosens Bioelectron 25:563–567
Sreenivasan K (2004) Imparting affinity sites for adenosine triphosphate on the surface of polyurethane through molecular imprinting. J Appl Polym Sci 94:2088–2090
Sallacan N, Zayats M, Bourenko T, Kharitonov AB, Willner I (2002) Imprinting of nucleotide and monosaccharide recognition sites in acrylamidephenylboronic acid-acrylamide copolymer membranes associated with electronic transducers. Anal Chem 74:702–712
Sessler JL, Melfi PJ, Pantos GD (2006) Uranium complexes of multidentate N-donor ligands. Coord Chem Rev 250:816–843
Rudkevich DM, Verboom W, Brzozka Z, Palys MJ, Stauthamer WPRV, Van Hummel GJ, Franken SM, Harkema S, Engbersen JFJ, Reinhoudt DN (1994) Functionalized UO2 salenes: neutral receptors for anions. J Am Chem Soc 116:4341–4351
Wojciechowski K, Wróblewski W, Brzózka Z (2003) Anion buffering in the internal electrolyte resulting in extended durability of phosphate-selective electrodes. Anal Chem 75:3270–3273
Kim J, Kang DM, Shin SC, Choi MY, Kim J, Lee SS, Kim JS (2008) Functional polyterthiophene-appended uranyl–salophen complex: electropolymerization and ion-selective response for monohydrogen phosphate. Anal Chim Acta 614:85–92
Wygladacz K, Qin Y, Wroblewski W, Bakker E (2008) Phosphate-selective fluorescent sensing microspheres based on uranyl salophene ionophores. Anal Chim Acta 614:77–84
Antonisse MMG, Snellink-Ruël BHM, Engbersen JFJ, Reinhoudt DN (1998) H2PO- 4-selective CHEMFETs with uranyl salophene receptors. Sens Actuators B 47:9–12
Wróblewski W, Wojciechowski K, Dybko A, Brzózka Z, Egberink RJM, Snellink-Ruël BHM, Reinhoudt DN (2000) Uranyl salophenes as ionophores for phosphate-selective electrodes. Sens Actuators B 68:313–318
Zhao M, Liao L, Wu M, Lin Y, **ao X, Nie C (2012) Double-receptor sandwich supramolecule sensing method for the determination of ATP based on uranyl–salophen complex and aptamer. Biosens Bioelectron 34:106–111
Zhang G, Yang M, Shen X, Chen L, Liao L (2013) Study on spectral properties of salophen–fluorescein and its uranyl complex. Appl Chem Ind 42:549–551
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC nos. 10975069, 11275091, 21101091, 11275090) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 706 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Liao, L., Zhang, G. et al. Determination of ATP using a double-receptor sandwich method based on molecularly imprinted membrane and fluorescence-labeled uranyl–salophen complex. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 7545–7551 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7217-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7217-2