Abstract
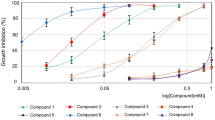
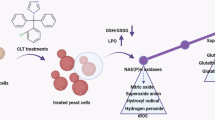
Ionic liquids (ILs) are interesting chemical compounds that have a wide range of industrial and scientific applications. They have extraordinary properties, such as the tunability of many of their physical properties and, accordingly, their activities; and the ease of synthesis methods. Hence, they became important building blocks in catalysis, extraction, electrochemistry, analytics, biotechnology, etc. This study determined antifungal activities of various imidazolium-based ionic liquids against yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae via minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) estimation method. Increasing the length of the alkyl group attached to the imidazolium cation, enhanced the antifungal activity of the ILs, as well as their ability of the disruption of the cell membrane integrity. FTIR studies performed on the S. cerevisiae cells treated with the ILs revealed alterations in the biochemical composition of these cells. Interestingly, the alterations in fatty acid content occurred in parallel with the increase in the activity of the molecules upon the increase in the length of the attached alkyl group. This trend was confirmed by statistical analysis and machine learning methodology. The classification of antifungal activities based on FTIR spectra of S. cerevisiae cells yielded a prediction accuracy of 83%, indicating the pharmacy and medicine industries could benefit from machine learning methodology. Furthermore, synthesized ionic compounds exhibit significant potential for pharmaceutical and medical applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alreqeb S, Ergüden B (2024) Chalcone derivatives disrupt cell membrane integrity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells and alter their biochemical composition. Arch Microbiol 206(1):34
Andrade JT, Santos FRS, Lima WG, Sousa CDF, Oliveira LSFM, Ribeiro RIMA, Gomes AJPS, Araújo MGF, Villar JAFP, Ferreira JMS (2018) Design, synthesis, biological activity and structure-activity relationship studies of chalcone derivatives as potential anti-Candida agents. J of Antibiotics 71:702–712
Avirdi E, Paumo HK, Kamdem BP, Singh MB, Kumari K, Katata-Seru L, Bahadur I (2023) Imidazolium-based ionic liquid-assisted silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity: experimental and density functional theory studies. ACS Omega 8(45):42976–42986
Baker MJ, Trevisan J, Bassan P, Bhargava R, Butler HJ, Dorling KM, Martin FL (2014) Using fourier transform IR spectroscopy to analyze biological materials. Nat Protoc 9(8):1771–1791
Bergamo VZ, Donato RK, Dalla Lana DF, Donato KJZ, Ortega GG, Schrekker HS, Fuentefria AM (2015) Imidazolium salts as antifungal agents: strong antibiofilm activity against multidrug-resistant Candida tropicalis isolates. Let Appl Microbiol 60(1):66–71
Borowiecki P, Milner-Krawczyk M, Brzezin′ska D, Wielechowska M, Plenkiewicz J (2013) Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of imidazolium and triazolium chiral ionic liquids. Eur J Org Chem 2013:712–720
Çelik F, Ünver Y, Aydın A, Güler Hİ, Bektaş Kİ (2024) Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of novel ionic liquids with bis-imidazole moieties: antitumor, antimicrobial effects and molecular docking studies. Org Commun 17(1):23–37
Charan KP, Ranjan P, Manojkumar K, Pothanagandhi N, Jha PC, Khedkar VM, Sivaramakrishna A, Vijayakrishna K (2015) Evaluation of imidazolium-based ionic liquids towards vermicidal activity: in vitro and in silico studies. RSC Adv 5(92):75415–75424
Cheng Y, Du Z, Zhu H, Guo X, He X (2016) Protective effects of arginine on Saccharomyces cerevisiae against ethanol stress. Sci Rep 6(1):31311
Cornellas A, Perez L, Comelles F, Ribosa I, Manresa A (2011) Self-aggregation and antimicrobial activity of imidazolium and pyridinium based ionic liquids in water solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 355:164–171
Corte L, Rellini P, Roscini L, Fatichenti F, Cardinali G (2010) Development of a novel, FTIR (fourier transform infrared spectroscopy) based, yeast bioassay for toxicity testing and stress response study. Anal Chim Acta 659(1–2):258–265
da Cunha RB, Fonseca LP, Calado CR (2021) Simultaneous elucidation of antibiotic mechanism of action and potency with high-throughput fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and machine learning. Appl Microbiol Biotech 105:1269–1286
Dalla Lana DF, Donato RK, Bündchen C, Guez CM, Bergamo VZ, de Oliveira LFS, Machado MM, Schrekker HS, Fuentefria AM (2015) Imidazolium salts with antifungal potential against multidrug-resistant dermatophytes. J Appl Microbiol 119(2):377–388
Egorova KS, Gordeev EG, Ananikov VP (2017) Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine. Chem Rev 117(10):7132–7189
Ergüden B, Lüleci HB, Ünver Y (2023) Chalcone Schiff bases disrupt cell membrane integrity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans cells. Arch Microbiol 205(6):246
Fojtášková J, Koutník I, Vráblová M, Sezimová H, Maxa M, Obalová L, Pánek P (2020) Antibacterial, antifungal and ecotoxic effects of ammonium and imidazolium ionic liquids synthesized in microwaves. Molecules 25(21):5181
Garcia-Gonzalez L, Geeraerd AH, Mast J, Briers Y, Elst K, Van Ginneken L, Van Impe JF, Devlieghere F (2010) Membrane permeabilization and cellular death of Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae as induced by high pressure carbon dioxide treatment. Food Microbiol 27(4):541–549
Gilmore BF, Earle MJ (2011) Development of ionic liquid biocides against microbial biofilm. Chim Oggi 29:50–53
Gravel J, Schmitzer AR (2017) Imidazolium and benzimidazolium-containing compounds: from simple toxic salts to highly bioactive drugs. Org Biomol Chem 15(5):1051–1071
Hossain CM, Ryan LK, Gera M, Choudhuri S, Lyle N, Ali KA, Diamond G (2022) Antifungals and drug resistance. Encyclopedia 2(4):1722–1737
Hryniewicka A, Niemirowicz-Laskowska K, Wielgat P, Car H, Hauschild T, Morzycki JW (2021) Dehydroepiandrosterone derived imidazolium salts and their antimicrobial efficacy. Bioorg Chem 108:104550
Iwai N, Nakauama K, Kitazume T (2011) Antibacterial activities of imidazolium, pyrrolidinium and piperidinium salts. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:1728–1729
Jung Y (2018) Multiple predicting K-fold cross-validation for model selection. J Nonparametric Stat 30(1):197–215
Kobayashi F, Odake S (2017) Intracellular acidification and damage of cellular membrane of Saccharomyces pastorianus by low-pressure carbon dioxide microbubbles. Food Control 71:365–370
Konuk H, Ergüden B (2020) Phenolic –OH group is crucial for the antifungal activity of terpenoids via disruption of cell membrane integrity. Folia Microbiol 65(4):775–783
Kumar Y, Wani FA, Ahmedi S, Shamsi A, Nadeem M, Manzoor N, Kamli MR, Malik MA, Rizvi MA, Patel R (2024) In vitro antifungal activity, cytotoxicity and binding analysis of imidazolium based ionic liquids with fluconazole: DFT and spectroscopic study. J Mol Liq 401:124631
Lockhart SR, Chowdhary A, Gold JAW (2023) The rapid emergence of antifungal-resistant human-pathogenic fungi. Nat Rev Microbiol 21:818–832
Luczak J, Jungnickel C, Laska I, Stolte S, Hupka J (2010) Antimicrobial and surface activity of 1-alkyl-3-methyl imidazolium derivatives. Green Chem 12:593–601
Mahapatra DK, Bharti SK, Asati V (2015) Chalcone scaffolds as anti-infective agents: Structural and molecular target perspectives. Eur J Med Chem 101:496–524
Messali M, Aouad MR, Ali AA, Rezki N, Ben Hadda T, Hammouti B (2015) Synthesis, characterization, and POM analysis of novel bioactive imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Med Chem Res 24:1387–1395
Mester P, Wagner M, Rossmanith P (2015) Antimicrobial effects of short chained imidazolium based ionic liquids – influence of anion chaotropicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 111:96–101
Osset-Trénor P, Pascual-Ahuir A, Proft M (2023) Fungal drug response and antimicrobial resistance. J Fungi 9(5):565
Pendleton JN, Gilmore BF (2015) The antimicrobial potential of ionic liquids: a source of chemical diversity for infection and biofilm control. Int J Antimicrob Agents 46:131–139
Pereira FO, Mendes JM, Lima EO (2013) Investigation on mechanism of antifungal activity of eugenol against Trichophyton rubrum. Med Mycology 51:507–513
Rabaan AA, Sulaiman T, Al-Ahmed SH, Buhaliqah ZA, Buhaliqah AA, AlYuosof B, Alfaresi M, Al Fares MA, Alwarthan S, Alkathlan MS et al (2023) Potential strategies to control the risk of antifungal resistance in humans: a comprehensive review. Antibiotics 12(3):608
Ranjan P, Kitawat BS, Singh M (2014) 1-Butylimidazole-derived ionic liquids: synthesis, characterisation and evaluation of their antibacterial, antifungal and anticancer activities. RSC Adv 4(96):53634–53644
Ranjan P, Athar M, Vijayakrishna K, Meena LK, Vasita R, Jha PC (2018a) Deciphering the anthelmintic activity of benzimidazolium salts by experimental and in-silico studies. J Mol Liq 268:156–168
Ranjan P, Athar M, Rather H, Vijayakrishna K, Vasita R, Jha PC (2018b) Appraisal of 1-Butylimidazole-derived ionic liquids as anthelmintic agents: an experimental and in silico approach. ChemistrySelect 3(26):7518–7526
Ranjan P, Athar M, Rather H, Vijayakrishna K, Vasita R, Jha PC (2018c) Rational design of imidazolium based salts as anthelmintic agents. J Mol Liq 255:578–588
Riduan SN, Zhang Y (2013) Imidazolium salts and their polymeric materials for biological applications. Chem Soc Rev 42(23):9055–9070
Sadeghi A, Jasour AM, Kowsari E, Gheibi M, Ghasemi MH, Ramakrishna S (2024) Comprehensive viewpoint on ionic liquids applications in sustainable pharmaceutical technology (experiments, simulations, and managerial insights). J Mol Liq 11:124991
Schrekker HS, Donato RK, Fuentefria AM, Bergamo V, Oliveirac LF, Machadoc MM (2013) Imidazolium salts as antifungal agents: activity against emerging yeast pathogens, without human leukocyte toxicity. Med Chem Comm 11:1457
Sikorski RS, Hieter P (1989) A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 122:9–27
Sivapragasam M, Moniruzzaman M, Goto M (2020) An overview on the toxicological properties of ionic liquids toward microorganisms. Biotech J 15(4):1900073
Sokolova M, Lapalme G (2009) A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Inf Proc Management 45(4):427–437
Trush MM, Semenyuta IV, Hodyna D, Ocheretniuk AD, Vdovenko SI, Rogalsky SP, Kalashnikova LE, Blagodatnyi V, Kobzar OL, Metelytsia LO (2020) Functionalized imidazolium-based ionic liquids: biological activity evaluation, toxicity screening, spectroscopic, and molecular docking studies. Med Chem Res 29:2181–2191
Venkata Nancharaiah Y, Kiran Kumar Reddy G, Lalithamanasa P, Venugopalan VP (2012) The ionic liquid 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium demonstrates comparable antimicrobial and antibiofilm behavior to a cationic surfactant. Biofouling 28:1141–1149
Vitiello A, Ferrara F, Boccellino M, Ponzo A, Cimmino C, Comberiati E, Zovi A, Clemente S, Sabbatucci M (2023) Antifungal drug resistance: an emergent health threat. Biomedicines 11(4):1063
Yu Y, Nie Y (2011) Toxicity and antimicrobial activities of ionic liquids with halogen anion. J Environ Prot 2:298–303
Zhang CW, Zhong XJ, Zhao YS, Rajoka MSR, Hashmi MH, Zhai P, Song X (2023) Antifungal natural products and their derivatives: a review of their activity and mechanism of actions. Pharm Res 7:100262
Zhu P, Li Y, Guo T, Liu S, Tancer RJ, Hu C, Zhao C, Xue C, Liao G (2023) New antifungal strategies: drug combination and co-delivery. Advanced Drug Deliv Rev 198:114874
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Ü. synthesized the compounds 1–7, F.T. and B.E. designed and performed the experiments. Y.Ü., F.T. and B.E. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
ERGÜDEN, B., TARLAK, F. & ÜNVER, Y. Imidazolium-based ionic liquids disrupt saccharomyces cerevisiae cell membrane integrity. Arch Microbiol 206, 334 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-04043-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-04043-y