Abstract
Summary
Vitamin D can improve muscle function and reduce falls, but whether it can strengthen neural connections within the brain and nervous system is not known. This 10-week randomised controlled trial indicates that treatment with 2,000 IU/day vitamin D3 does not significantly alter neuroplasticity relative to placebo in older adults.
Introduction
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of vitamin D supplementation on neuroplasticity, serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and muscle strength and function in older adults.
Methods
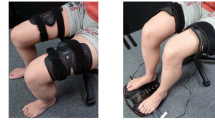
This was a 10-week double-blinded, placebo-controlled randomised trial in which 26 older adults with 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25OHD] concentrations 25–60 nmol/L were randomised to 2,000 IU/day vitamin D3 or matched placebo. Single- and paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation applied over the motor cortex was used to assess changes in motor-evoked potentials (MEPs) and short-interval intracortical inhibition (SICI), as measures of corticospinal excitability and inhibition respectively, by recording electromyography (EMG) responses to stimulation from the wrist extensors. Changes in muscle strength, stair climbing power, gait (timed-up-and-go), dynamic balance (four square step test), serum 25(OH)D and BDNF concentrations were also measured.
Results
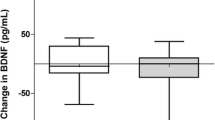
After 10 weeks, mean 25(OH)D levels increased from 46 to 81 nmol/L in the vitamin D group with no change in the placebo group. The vitamin D group experienced a significant 8–11 % increase in muscle strength and a reduction in cortical excitability (MEP amplitude) and SICI relative to baseline (all P < 0.05), but these changes were not significantly different from placebo. There was no effect of vitamin D on muscle power, function or BDNF.
Conclusions
Daily supplementation with 2,000 IU vitamin D3 for 10 weeks had no significant effect on neuroplasticity compared to placebo, but the finding that vitamin D treatment alone was associated with a decrease in corticospinal excitability and intracortical inhibition warrants further investigation as this suggests that it may improve the efficacy of neural transmission within the corticospinal pathway.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Dawson-Hughes B, Staehelin HB, Orav JE, Stuck AE, Theiler R, Wong JB, Egli A, Kiel DP, Henschkowski J (2009) Fall prevention with supplemental and active forms of vitamin D: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 339:b3692
Muir SW, Montero-Odasso M (2011) Effect of vitamin D supplementation on muscle strength, gait and balance in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc 59:2291–2300
Bischoff HA, Borchers M, Gudat F, Duermueller U, Theiler R, Stahelin HB, Dick W (2001) In situ detection of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor in human skeletal muscle tissue. Histochem J 33:19–24
Sorensen OH, Lund B, Saltin B, Lund B, Andersen RB, Hjorth L, Melsen F, Mosekilde L (1979) Myopathy in bone loss of ageing: improvement by treatment with 1 alpha-hydroxycholecalciferol and calcium. Clin Sci (Lond) 56:157–161
Endo I, Inoue D, Mitsui T, Umaki Y, Akaike M, Yoshizawa T, Kato S, Matsumoto T (2003) Deletion of vitamin D receptor gene in mice results in abnormal skeletal muscle development with deregulated expression of myoregulatory transcription factors. Endocrinology 144:5138–5144
Annweiler C, Schott AM, Berrut G, Chauvire V, Le Gall D, Inzitari M, Beauchet O (2010) Vitamin D and ageing: neurological issues. Neuropsychobiology 62:139–150
Eyles DW, Smith S, Kinobe R, Hewison M, McGrath JJ (2005) Distribution of the vitamin D receptor and 1 alpha-hydroxylase in human brain. J Chem Neuroanat 29:21–30
Groppa S, Oliviero A, Eisen A, Quartarone A, Cohen LG, Mall V, Kaelin-Lang A, Mima T, Rossi S, Thickbroom GW, Rossini PM, Ziemann U, Valls-Sole J, Siebner HR (2012) A practical guide to diagnostic transcranial magnetic stimulation: report of an IFCN committee. Clin Neurophysiol 123:858–882
Weier AT, Kidgell DJ (2012) Strength training with superimposed whole body vibration does not preferentially modulate cortical plasticity. ScientificWorldJournal 2012:876328
Ni Z, Chen R (2008) Short-interval intracortical inhibition: a complex measure. Clin Neurophysiol 119:2175–2176
Li Voti P, Conte A, Suppa A, Iezzi E, Bologna M, Aniello MS, Defazio G, Rothwell JC, Berardelli A (2011) Correlation between cortical plasticity, motor learning and BDNF genotype in healthy subjects. Exp Brain Res 212:91–99
Horch HW, Katz LC (2002) BDNF release from single cells elicits local dendritic growth in nearby neurons. Nat Neurosci 5:1177–1184
Lipsky RH, Marini AM (2007) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neuronal survival and behavior-related plasticity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1122:130–143
Fritsch B, Reis J, Martinowich K, Schambra HM, Ji Y, Cohen LG, Lu B (2010) Direct current stimulation promotes BDNF-dependent synaptic plasticity: potential implications for motor learning. Neuron 66:198–204
Kujirai T, Caramia MD, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Ferbert A, Wroe S, Asselman P, Marsden CD (1993) Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol 471:501–519
Lazowski DA, Ecclestone NA, Myers AM, Paterson DH, Tudor-Locke C, Fitzgerald C, Jones G, Shima N, Cunningham DA (1999) A randomized outcome evaluation of group exercise programs in long-term care institutions. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 54:M621–M628
Stewart AL, Mills KM, King AC, Haskell WL, Gillis D, Ritter PL (2001) CHAMPS physical activity questionnaire for older adults: outcomes for interventions. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:1126–1141
Ziemann U (2013) Pharmaco-transcranial magnetic stimulation studies of motor excitability. Handb Clin Neurol 116:387–397
Wrzosek M, Lukaszkiewicz J, Wrzosek M, Jakubczyk A, Matsumoto H, Piatkiewicz P, Radziwon-Zaleska M, Wojnar M, Nowicka G (2013) Vitamin D and the central nervous system. Pharmacol Rep 65:271–278
Chabas JF, Alluin O, Rao G, Garcia S, Lavaut MN, Risso JJ, Legre R, Magalon G, Khrestchatisky M, Marqueste T, Decherchi P, Feron F (2008) Vitamin D2 potentiates axon regeneration. J Neurotrauma 25:1247–1256
Bianco J, Gueye Y, Marqueste T, Alluin O, Risso JJ, Garcia S, Lavault MN, Khrestchatisky M, Feron F, Decherchi P (2011) Vitamin D3 improves respiratory adjustment to fatigue and H-reflex responses in paraplegic adult rats. Neuroscience 188:182–192
Chen XY, Carp JS, Chen L, Wolpaw JR (2002) Corticospinal tract transection prevents operantly conditioned H-reflex increase in rats. Exp Brain Res 144:88–94
Skaria J, Katiyar BC, Srivastava TP, Dube B (1975) Myopathy and neuropathy associated with osteomalacia. Acta Neurol Scand 51:37–58
Daskalakis ZJ, Fitzgerald PB, Christensen BK (2007) The role of cortical inhibition in the pathophysiology and treatment of schizophrenia. Brain Res Rev 56:427–442
Floeter MK, Rothwell JC (1999) Releasing the brakes before pressing the gas pedal. Neurology 53:664–665
Coxon JP, Stinear CM, Byblow WD (2007) Selective inhibition of movement. J Neurophysiol 97:2480–2489
Buell JS, Dawson-Hughes B (2008) Vitamin D and neurocognitive dysfunction: preventing “D”ecline? Mol Aspects Med 29:415–422
Zehnder D, Bland R, Williams MC, McNinch RW, Howie AJ, Stewart PM, Hewison M (2001) Extrarenal expression of 25-hydroxyvitamin d(3)-1 alpha-hydroxylase. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:888–894
Feron F, Burne TH, Brown J, Smith E, McGrath JJ, Mackay-Sim A, Eyles DW (2005) Developmental vitamin D3 deficiency alters the adult rat brain. Brain Res Bull 65:141–148
Jones EG (1993) GABAergic neurons and their role in cortical plasticity in primates. Cereb Cortex 3:361–372
Diamond T, Wong YK, Golombick T (2013) Effect of oral cholecalciferol 2,000 versus 5,000 IU on serum vitamin D, PTH, bone and muscle strength in patients with vitamin D deficiency. Osteoporos Int 24:1101–1105
Pfeifer M, Begerow B, Minne HW, Suppan K, Fahrleitner-Pammer A, Dobnig H (2009) Effects of a long-term vitamin D and calcium supplementation on falls and parameters of muscle function in community-dwelling older individuals. Osteoporos Int 20:315–322
Stockton KA, Mengersen K, Paratz JD, Kandiah D, Bennell KL (2011) Effect of vitamin D supplementation on muscle strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 22(3):859–871
Dhesi JK, Bearne LM, Moniz C, Hurley MV, Jackson SH, Swift CG, Allain TJ (2002) Neuromuscular and psychomotor function in elderly subjects who fall and the relationship with vitamin D status. J Bone Miner Res 17:891–897
Weier AT, Pearce AJ, Kidgell DJ (2012) Strength training reduces intracortical inhibition. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 206:109–119
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Blackmores for providing the vitamin D and placebo capsules for the trial. We wish to thank Belinda De Ross for her assistance with the physiological testing.
Grants
None.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pirotta, S., Kidgell, D.J. & Daly, R.M. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on neuroplasticity in older adults: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled randomised trial. Osteoporos Int 26, 131–140 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-014-2855-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-014-2855-6