Abstract
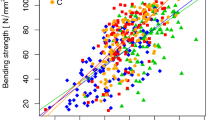
NIR predictions of cellulose content and stiffness (modulus of elasticity, MOE) from spectra collected from the radial longitudinal surface of Eucalyptus globulus wood were found to be reliable indicators of zones of non-recoverable collapse associated with the presence of tension wood. Radial sections from 25 quarter-sawn boards cut from plantation-grown E. globulus trees in Spain were scanned to generate radial profiles of NIR-predicted wood properties at 2 mm increments. These boards manifested a range of non-recoverable collapse features, from no collapse to one or more severe collapse bands. Collapse bands occurred where NIR-predicted cellulose content and MOE exceeded threshold levels of 50 % and 25 GPa, respectively for more than four consecutive millimetres. A non-recoverable collapse indicator provided a clear predictor of non-recoverable collapse. A NRCI value ≥100 for a consecutive interval of at least 4 mm successfully predicted all ten NRC bands with shrinkage ≥10 % of board thickness. The potential applications of this tension wood detection method are discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruker (2005) OPUS 5.5. Ettlingen, Germany, Bruker Optik
Chafe S (1986) Radial variation of collapse, volumetric shrinkage, moisture conent and density in Eucalyptus regnans F. Muell. Wood Sci Technol 20(3):253–262
Dadswell H, Wardrop A (1949) What is reaction wood? Aust For 13(1):22–33
Downes GM, Meder R, Ebdon N, Evans R, Southerton S, Joyce K, Bond H (2010) Radial variation in cellulose content and kraft pulp yield in Eucalyptus nitens using NIR spectral analysis of air-dry wood surfaces. JNIRS 18(2):147–156
Downes GM, Harwood CE, Wiedemann J, Ebdon N, Bond H, Meder R (2012) Radial variation in kraft pulp yield and cellulose content in Eucalyptus globulus wood across three contrasting sites predicted by near infrared spectroscopy. Can J For Res 42(8):1577–1586
Evans R (2008) Wood stiffness by X-ray diffractometry. In: Stokke DD, Groom L (eds) Characterization of the cellulosic cell wall. Wiley, pp 138–146
Goswami L, Dunlop JW, Jungnikl K, Eder M, Gierlinger N, Coutand C, Jeronimidis G, Fratzl P, Burgert I (2008) Stress generation in the tension wood of poplar is based on the lateral swelling power of the G-layer. Plant J 56(4):531–538
Jacobs MR (1955) Growth habits of the eucalypts, Forestry and Timber Bureau, Department of the Interior, Commonwealth of Australia
Kubler H (1988) Silvicultural control of mechanical stresses in trees. Can J For Res 18(10):1215–1225
Malan F, Gerischer G (1987) Wood property differences in South African grown Eucalyptus grandis trees of different growth stress intensity. Holzforschung 41(6):331–335
Martens H, Næs T (1989) Multivariate calibration. Wiley, Chichester
Meder R, Marston D, Ebdon N, Evans R (2010) Spatially-resolved radial scanning of tree increment cores for near infrared prediction of microfibril angle and chemical composition. J Near Infrared Spectrosc 18(6):499
Nutto L, Touza MC (2004) Production of high quality sawn-timber from Eucalyptus globulus (In Spanish) CIS-Madera 12: 6–18
Raymond CA, Kube PD, Pinkard L, Savage L, Bradley AD (2004) Evaluation of non-destructive methods of measuring growth stress in Eucalyptus globulus: relationships between strain, wood properties and stress. For Ecol Manag 190(2):187–200
R-Core-Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing, R version 2.15.1. R Foundation for 607 Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org. Accessed 16 Oct 2012
Schimleck L (2008) Near infrared spectroscopy: a rapid, non-destructive method for measuring wood properties and its application to tree breeding. NZ J For Sci 38(1):14–35
Touza M (2001) Research project about sawing systems suitable for processing Eucalyptus globulus with high growth stresses (In Spanish). CIS-Madera 6:8–37
Tsuchikawa S (2007) A review of recent near infrared research for wood and paper. Appl Spectrosc Rev 42(1):43–71
Tsuchikawa S, Schwanninger M (2011) A review of recent near-infrared research for wood and paper (Part 2). Appl Spectrosc Rev 48(7):560–587
Wardrop A, Dadswell H (1955) The nature of reaction wood. IV. Variations in cell wall organization of tension wood fibres. Aust J Bot 3(2):177–189
Washusen R, Evans R (2001a) The association between cellulose crystallite width and tension wood occurrence in Eucalyptus globulus. IAWA J 22(3):235–244
Washusen R, Evans R (2001b) Prediction of wood tangential shrinkage from cellulose crystallite width and density in one 11-year-old tree of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Aust For 64(2):123–126
Washusen R, Evans R (2002) The measurement of cellulose crystallite width by X-ray diffraction on SilviScan-2 and its possible application in eucalypt and acacia species. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium. Wood Structure and Properties. 2: 1–3
Washusen R, Ilic J (2001) Relationship between transverse shrinkage and tension wood from three provenances of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Holz Roh-Werkst 59(1–2):85–93
Washusen R, Blakemore P, Northway R, Vinden P, Waugh G (2000) Recovery of dried appearance grade timber from Eucalyptus globulus Labill, grown in plantations in medium rainfall areas of the southern Murray-Darling Basin. Aust For 63(4):277–283
Washusen R, Ades P, Vinden P (2002) Tension wood occurrence in Eucalyptus globulus Labill. I. The spatial distribution of tension wood in one 11-year-old tree. Aust For 65(2):120–126
Washusen R, Ilic J, Waugh G (2003) The relationship between longitudinal growth strain, tree form and tension wood at the stem periphery of ten-to eleven-year-old Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Holzforschung 57(3):308–316
Washusen R, Baker T, Menz D, Morrow A (2005) Effect of thinning and fertilizer on the cellulose crystallite width of Eucalyptus globulus. Wood Sci Technol 39(7):569–578
Washusen R (2013) Processing methods for production of solid wood products from plantation-grown Eucalyptus species of importance to Australia. Melbourne, Australia, Forest and Wood Products Australia
Wentzel-Vietheer M, Washusen R, Downes GM, Harwood C, Ebdon N, Ozarska B, Baker T (2013) Prediction of non-recoverable collapse in Eucalyptus globulus from near infrared scanning of radial wood samples. Eur J Wood Prod 71(6):755–768
Yang JL (2007) Investigation of potential sawlog quality indicators––a case study with 32-year-old plantation Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Holz Roh-Werkst 65(6):419–427
Yang J-L, Fife D, Waugh G, Downes G, Blackwell P (2002) The effect of growth strain and other defects on the sawn timber quality of 10-year-old Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Aust For 65(1):31–37
Yang JL, Bailleres H, Evans R, Downes G (2006) Evaluating growth strain of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. from SilviScan measurements. Holzforschung 60(5):574–579
Acknowledgments
This study was carried out with support from CRC Forestry Ltd. (Hobart, Tasmania), the National Centre for Future Forest Industries, University of Tasmania, CIS Madera (Galicia, Spain) and Forest Quality Pty. Ltd. (Franklin, Tasmania). The research done by CIS Madeira has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme under grant agreement No. 284181 (“Trees4Future”). The contents of this publication reflect only the authors’ views and the European Union is not liable for any use that may be made of the information contained therein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Downes, G.M., Touza, M., Harwood, C. et al. NIR detection of non-recoverable collapse in sawn boards of Eucalyptus globulus . Eur. J. Wood Prod. 72, 563–570 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-014-0813-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-014-0813-9