Abstract
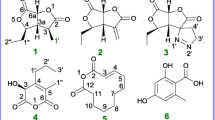
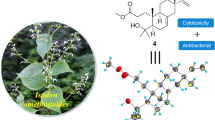
Four known metabolites, macrophin (1), rosellisin (2), 2-(2-hydroxy-5-6-methoxy-3-methylene-1,4-benzodioxin-2(3H)-one (3), and methoxyphenoxyacrylic acid (4) were isolated, for the first time, from an endophytic fungus, Phoma macrostoma inhabiting the inner tissue of medicinal plant Glycyrrhiza glabra Linn. Their structures were characterized by comparison of their NMR data with literature data, and X-ray diffraction data of macrophin (1) as described herein for the first time. The compounds (1–4) were evaluated for their growth-inhibitory activities against a panel of cancer cell lines. Of these substances, macrophin (1) showed prominent cytotoxic activity against the MDA-MB-231, T47D, MCF-7, and MIAPaCa-2 cancer-cell lines with IC50 values of 14.8, 8.12, 13.0, and 0.9 μM, respectively. This biological significance has prompted us to generate a series of five acylated analogs (1a–1e) of 1 to conduct structure–activity relationship (SAR) study. The result illustrates all the analogues (1a–1e) were more potent than 1 against MDMB-231 and MIAPaCa-2 cancer cell lines. The compound 1d, an n-butanoyl substituent, has been proven to be three-fold more potent than 1 with IC50 values of 0.3 and 3.7 µM against MIAPaCa-2 and MDMB-231 cell lines, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almasan A, Yin Y, Kelly RE, Lee EY, Bradley A, Li W, Bertino JR, Wahl GM (1995) Deficiency of retinoblastoma protein leads to inappropriate S-phase entry, activation of E2F-responsive genes, and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5436–5440
Alurappa RCS, Narayanaswamy R, Sinniah UR, Mohanty SK, Swamy MK (2018) Endophytic fungi and bioactive metabolites production: an update. In: Patra J, Das G, Shin HS(eds) Microbial Biotechnology. Springer, Singapore
Arora P, Wani ZA, Nalli Y, Ali A, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S (2016) Antimicrobial potential of Thiodiketopiperazine derivatives produced by Phoma sp., an endophyte of Glycyrrhiza glabra Linn. Microb Ecol 72:802–812
Assante G, Camarda L, Merlini L, Nasini G (1981) Secondary metabolites from Mycosphaerella ligulicola. Phytochemistry 20:1955–1957
Aveskamp MM, de Gruyter J, Woudenberg JHC, Verkley GJM, Crous PW (2010) Highlights of the Didymellaceae: a polyphasic approach to characterise Phoma and related pleosporalean genera. Stud Mycol 65:1–60
Bennett A, Ponder M, Garcia-Diaz J (2018) Phoma infections: classification, potential food sources, and their clinical impact. Microorganisms 6:58
Butler MS (2004) The role of natural product chemistry in drug discovery. J Nat Prod 67:2141–2153
Butler MS (2005) Natural products to drugs: natural product derived compounds in clinical trials. Nat Prod Rep 22:162–195
Crombie L, Crombie WML, Jamieson SV, Palmer CJ (1988) Acid catalyzed terpenylations of olivetol in the synthesis of cannabinoids. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1:1243–1250
Estrov Z, Shishodia S, Faderl S, Harris D, Van Q, Kantarjian HM, Talpaz M, Aggarwal BB (2003) Resveratrol blocks interleukin-1beta-induced activation of the nuclear transcription factor NF-kappaB, inhibits proliferation, causes S-phase arrest, and induces apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 102:987–995
Fulda S, Debatin KM (2006) Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 25:4798
Gerl R, Vaux DL (2005) Apoptosis in the development and treatment of cancer. Carcinogenesis 26:263–270
Graupner PR, Carr A, Clancy E, Gilbert J, Bailey KL, Derby JA, Gerwick BC (2003) The macrocidins: novel cyclic tetramic acids with herbicidal activity produced by Phoma macrostoma. J Nat Prod 66:1558–1561
Jia M, Chen L, **n H-L, Zheng C-J, Rahman K, Han T, Qin L-P (2016) A friendly relationship between endophytic fungi and medicinal plants: a systematic review. Front Microbiol 7:906
Kumar S, Guru SK, Venkateswarlu V, Malik F, Vishwakarma RA, Sawant SD, Bhushan S (2015) A novel quinoline based second-generation mTOR inhibitor that induces apoptosis and disrupts PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 15:1297–1304
Kusari S, Hertweck C, Spiteller M (2012) Chemical ecology of endophytic fungi: origins of secondary metabolites. Chem Biol 19:792–798
Nair MSR (1976) Biogenesis and revised structure of rosellisin; structure of rosellisin aldehyde. Phytochemistry 15:1090–1091
Nalli Y, Arora P, Wadhwa B, Malik FA, Vishwakarma RA, Gupta VK, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S, Ali A (2017) Diapolic acid A-B from an endophytic fungus, Diaporthe terebinthifolii depicting antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity. J Antibiot 70:212–215
Nalli Y, Mirza DN, Wani ZA, Wadhwa B, Mallik FA, Raina C, chaubey A, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S, Ali A (2015) Phialomustin A–D, new antimicrobial and cytotoxic metabolites from an endophytic fungus, Phialophora mustea. RSC Adv 5:95307–95312
Pusztahelyi T, Holb I, Pócsi I (2015) Secondary metabolites in fungus–plant interactions. Front Plant Sci 6:573
Qadri M, Rajput R, Abdin MZ, Vishwakarma RA, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S (2014) Diversity, molecular phylogeny, and bioactive potential of fungal endophytes associated with the Himalayan blue pine (Pinus wallichiana). Microb Ecol 67:877–887
Rubinsztein DC, Gestwicki JE, Murphy LO, Klionsky DJ (2007) Potential therapeutic applications of autophagy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:304–312
Strobel G, Singh SK, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S, Mitchell AM, Geary B, Sears J (2011) An endophytic/pathogenic Phoma sp. from creosote bush producing biologically active volatile compounds having fuel potential. FEMS Microbiol Lett 320:87–94
Wang X, Zhou H, Chen H, **g X, Zheng W, Li R, Sun T, Liu J, Fu J, Huo L, Li Y-z, Shen Y, Ding X, Müller R, Bian X, Zhang Y (2018) Discovery of recombinases enables genome mining of cryptic biosynthetic gene clusters in Burkholderiales species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E4255–E4263
Acknowledgements
PA is supported by the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India through INSPIRE Senior Research Fellowship. PA and SK acknowledge AcSIR for their enrollment in the Ph.D. program. The authors would like to acknowledge the Ministry of AYUSH (New Delhi) for providing financial support for the work of YN (Z.28015/229/2015-HCP EMR). The article bears the institutional manuscript no. IIIM/2271/2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nalli, Y., Arora, P., Khan, S. et al. Isolation, structural modification of macrophin from endophytic fungus Phoma macrostoma and their cytotoxic potential. Med Chem Res 28, 260–266 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-018-2281-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-018-2281-y