Abstract
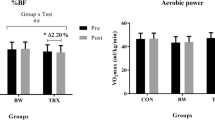
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of a multidisciplinary body mass reduction (BMR) program on body composition, muscle function and motor performance in 50 obese [mean body mass index (BMI): 35.9±5.8 kg/m2] boys and girls aged 12-17 yr (Tanner stage III, IV and V). The hospital-based BMR program combined an energy-restricted diet (1400-1600 kcal), nutritional education, psychological counselling and moderate physical activity (45-60 min/session; 5 sessions/week; 60-80% of the maximal heart rate) during a 3-week period. Fat mass, fatfree mass, maximal power during jum** and stair climbing as well as maximal strength of the upper and lower limb muscles were quantified before and after the treatment. Body mass and fat mass significantly decreased following the BMR program, respectively −5.1 and −7.8% (p<0.001), while percent fat-free mass increased 2.3% (p<0.001). The treatment significantly increased both stair climbing and jum** power, respectively 8.2 and 8.9% (p<0.05), and the same was true for maximal strength of the upper and lower limb muscles (p<0.001). For the first time, it was demonstrated that a BMR program entailing diet and physical exercise significantly improved body composition, muscle function and motor performance in obese boys and girls aged 12-17 yr, while gender and pubertal stages had no influence on BMR program-induced changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Troiano RP, Flegal KM, Kuczmarski RJ, Campbell SM, Johnson CL. Overweight prevalence and trends for children and adolescents. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1963 to 1991. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1991, 149: 1085–91.
Dietz WH. Health consequences of obesity in youth: childhood predictors of adult disease. Pediatrics 1998, 101: 518–25.
Must A, Strauss RS. Risk and consequences of childhood and adolescent obesity. Int J Obes 1999, 23: S2–11.
Parizkova J, Hills AP. Childhood obesity: prevention and treatment. Boca Raton: CRC press LLC 2001, 421–2.
Gutin B, Cucuzzo N, Islam S, Smith C, Moffatt R, Pargman D. Physical training improves body composition of black obese 7- to 11-year-old girls. Obes Res 1995, 3: 305–12.
Treuth MS, Hunter GR, Pichon C, Figueroa-Colon R, Goran MI. Fitness and energy expenditure after strength training in obese prepubertal girls. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998, 30: 1130–6.
Treuth MS, Hunter GR, Figueroa-Colon R, Goran MI. Effect of strength training on intra-abdominal adipose tissue in obese prepubertal girls. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998, 30: 1738–43.
Figueroa-Colon R, Franklin FA, Lee JY, von Almen TK, Suskind RM. Feasibility of a clinic-based hypocaloric dietary intervention implemented in a school setting for obese children. Obes Res 1996, 4: 419–29.
Maffeis C, Schutz Y, Pinelli L. Effect of weight loss on resting energy expenditure in obese prepubertal children. Int J Obes 1992, 16: 41–7.
Zwiauer K, Schmidinger H, Klicpera M, Mayr H, Widhalm K. 24-hours electrocardiographic monitoring in obese children and adolescents during 3 weeks of low calorie diet (500 kcal). Int J Obes 1989, 13: 101–5.
Deforche B, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Debode P, et al. Changes in fat mass, fat-free mass and aerobic fitness in severely obese children and adolescents following a residential treatment programme. Eur J Pediatr 2003, 162: 616–22.
Eliakim A, Kaven G, Berger I, Friedland O, Wolach B, Nemet D. The effect of a combined intervention on body mass index and fitness in obese children and adolescents — a clinical experience. Eur J Pediatr 2003, 161: 449–54.
Epstein LH, Wing RR, Penner BC, Kress MJ. The effect of diet and controlled exercise on weight loss in obese children. J Pediatr 1985, 107: 358–61.
Suskind R, Blacker U, Udall Jr J, et al. Recent advances in the treatment of childhood obesity. Pediatr Diabetes 2000, 1: 23–33.
Sartorio A, Lafortuna CL, Massarini M, Galvani C. Effects of different training protocols on exercise performance during a short-term body weight reduction programme in severely obese patients. Eat Weight Disord 2003; 8: 36–43.
Cacciari E, Milani S, Balsamo A, et al. Italian cross-sectional growth charts for height, weight and BMI (6-20 y). Eur J Clin Nutr 2002, 56: 171–80.
Lukaski HC, Bolonchuk WW, Hall CB, Siders WA. Validation of tetrapolar bioelectrical measurements to assess human body composition. J Appl Physiol 1986, 60: 1327–32.
Gray DS, Bray GA, Gemayel N, Kaplan K. Effects of obesity on bioelectrical impedance. Am J Clin Nutr 1989, 50: 255–60.
Margaria R, Aghemo P, Rovelli E. Measurement of muscular power (anaerobic) in man. J Appl Physiol 1966, 21: 1662–4.
Sartorio A, Lafortuna CL, Conte G, Faglia G, Narici MV. Changes in motor control and performance after a short term body mass reduction program in obese subjects. J Endocrinol Invest 2001, 24: 393–8.
Lafortuna CL, Fumagalli E, Vangeli V, Sartorio A. Lower limb alactic anaerobic power output assessed with different techniques in morbid obesity. J Endocrinol Invest 2002, 25: 134–41.
Asmussen E, Bonde-Petersen F. Storage of elastic energy in skeletal muscles in man. Acta Physiol Scand 1974, 91: 385–92.
Bosco C, Luthanen P, Komi PV. A simple method for measurement of mechanical power in jum**. Eur J Appl Physiol 1983, 50: 273–82.
Mayhew JL, Prinster JL, Ware JS, Zimmer DL, Arabas JR, Bemben MG. Muscular endurance repetitions to predict bench press strength in men of different training levels. J Sport Med Phys Fitness 1995, 35: 108–13.
Winters-Stone KM, Snow CM. Musculoskeletal response to exercise is greatest in women with low initial values. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2003, 35: 1691–6.
Lafortuna CL, Resnik M, Galvani C, Sartorio A. Effects of non-specific vs individualized exercise training protocols on aerobic, anaerobic and strength performance in severely obese subjects during a short-term body mass reduction program. J Endocrinol Invest 2003, 26: 197–205.
Sartorio A, Fontana P, Trecate L, Lafortuna CL. Short-term changes of fatigability and muscle performance in severe obese patients after an integrated body mass reduction program. Diab Nutr Metab 2003; 16: 88–93.
Sartorio A, Maffiuletti NA, Agosti F, Marinone PG, Ottolini S, Lafortuna CL. Body mass reduction markedly improves muscle performance and body composition in obese females aged 61-75 years: comparison between the effects exerted by energy-restricted diet plus moderate aerobic-strength training alone or associated with rec-GH or nandrolone undecanoate. Eur J Endocrinol 2004, 105: 511–5.
Barbeau P, Gutin B, Litaker M, Owens S, Riggs S, Okuyama T. Correlates of individual differences in body-composition changes resulting from physical training in obese children. Am J Clin Nutr 1999, 69: 705–11.
Schwingshandl J, Sudi K, Eibl B, Wallner S, Borkenstein M. Effect of an individualised training programme during weigth reduction on body composition: a randomised trial. Arch Dis Child 1999, 81: 426–8.
Schwingshandl J, Borkenstein M. Changes in lean body mass in obese children during a weight reduction program: effect on short term and long term outcome. Int J Obes 1995, 19: 752–5.
Sartorio A, Agosti F, Resnik M, Lafortuna CL. Effect of a 3-wk integrated body weight reduction program on leptin levels and body composition in severe obese subjects. J Endocrinol Invest 2003, 26: 250–6.
Tounian P, Frelut M-L, Parlier G, et al. Weight loss and changes in energy metabolism in massively obese adolescents. Int J Obes 1999, 23: 830–7.
Gutin B, Barbeau P, Owens S, et al. Effects of exercise intensity on cardiovascular fitness, total body composition, and visceral adiposity of obese adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr 2002, 75: 818–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maffiuletti, N.A., De Col, A., Agosti, F. et al. Effect of a 3-week body mass reduction program on body composition, muscle function and motor performance in pubertal obese boys and girls. J Endocrinol Invest 27, 813–820 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346274
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346274