Summary
A pharmacokinetic study with 30 mg propiverine p.o. was performed in healthy volunteers (10 males, 6 females, age 36–56 years, body weight 55–100 kg, body height 162–184 cm, Broca index 0.96–1.19). 8 of them were poor and 8 extensive metabolizers of the debrisoquine type hydroxylation polymorphism. The total anticholinergic activity of the parent compound and active metabolites was measured with a radioreceptor assay calibrated with the metabolite M2. The affinity of this metabolite to the muscarinic receptors was similar to that of atropine. The urinary excretion of 3 major metabolites was determined with TLC and densitometry. Arterial blood pressure, heart rate, diameter of pupils, accommodation and parotic salivary flow were also measured.
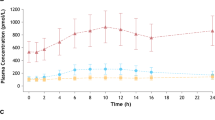
The concentrations of anticholinergic equivalents of propiverine were below 1 ng/ml of M2. 1.4–6.0% of the dose were excreted as N-oxidized metabolites into the urine. The poor and extensive metabolizers of debrisoquine did not differ significantly with regard to the concentration time behaviour of the active drug components, pattern of major metabolites, adverse drug reactions or any pharmacodynamic parameters measured.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beier R., Herbst A., Knauff G., et al. (1976): Die klinische Erprobung von α,α-Diphenyl-n-propoxyessigsäure-4-(1-methylpiperidyl)-ester (P4), einem Antiparkinsonmittel. Zbl. Pharm. Pharmakother. Labor-Diagn., 115, 603–609.
Wehnert J., Kelly L.U., Sage S. (1981): Zur Therapie der Detrusorhyperaktivität mit Propiverin (Mictonorm®). Z. Urol. Nephrol. 74, 827–832.
Blau U., Retzke U. (1984): Behandlung von Urge-Symptomatik und Urge-Inkontinenz mit Propiverinhydrochlorid (Mictonorm®). Zbl. Gynäkol., 106, 981–987.
Höfner K., Dorschner W., Höfner T., Dieterich F. (1985): Die Veränderung der Urodynamik des Detrusors bei Frauen mit Urge-Symptomatik durch Mictonorm®. Z. Urol. Nephrol., 78, 363–370.
Otto-Unger G. (1985): Zur Behandlung der instabilen Blase des Kindes mit dem Anticholinergikum Propiverinhydrochlorid (Mictonorm®/Mictonetten®). Z. Urol. Nephrol., 78, 145–152.
Voigt R., Voigt P., Kunath H., Al Hasan A. (1986): Unsere Erfahrung mit der konservativ-medikamentösen Therapie der Drang-Symptomatik der Frau. Z. Urol. Nephrol., 79, 197–205.
Vietinghoff G., Hammer S. (1981): Untersuchungen der antispasmodischen Wirkung von α,α-Diphenyl-, n-propoxyessigsäure-4-(1-methylpiperidyl)-ester (Mictonorm®) and der isolierten Meerschweinchenblase. Zbl. Pharm. Pharmakother. Labor-Diagn., 120, 1219–1224.
Riotte J., Mutschler E. (1987): Untersuchungen zur spasmolytischen Aktivität von Propiverin und einigen Strukturanaloga. Arzneimittelforsch., 37, 300–302.
Kaneko H., Kitazato K., Yamazaki Y., Okada H. (1989): Mode of inhibitory action of propiverine hydrochloride on the micturation movements of the bladder in dogs. Fol. Pharmacol. Jpn, 94, 151–157.
Kaneko S., Kitazato K., Yamazaki Y., Okada H., Nagai M. (1990): Effect of propiverine hydrochloride on the function of the bladder in decerebrated dogs. Fol. Pharmacol. Jpn, 95, 55–61.
Nomura N., Kaneko S., Hamakawa T., Nagai M., Iriki M. (1989): Effects of propiverine hydrochloride (P-4) and its metabolites on urinary bladder function in anesthetized rats. Fol. Pharmacol. Jpn, 94, 173–180.
Haruno A., Yamasaki Y., Miyoshi K., et al. (1989): Effect of propiverine hydrochloride and its metabolites on isolated guinea pig urinary bladder. Fol. Pharmacol. Jpn, 94, 145–150.
Siegmund W., Nigussie M., Tilahun K., Aitenfissu H., Franke G., Wengler A. (1990): Anticholinergic properties of propiverine and its metabolites. Pharmazie, 45, 67–68.
Kugimiya T. (1985): Propiverine phase-I-study. P4-meeting, Tokyo.
Marunaka T., Umeno Y., Minami Y., et al. (1987): Gas chromatographic-mass fragmentographic determination of propiverine and its metabolites in plasma and urine. J. Chromatrogr., 420, 43–52.
Haustein K.O., Hüller G. (1987): On the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of propiverine in man. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet., 13, 81–90.
Göber B., Dressler K., Franke P. (1988): Zur Biotransformation von Propiverinhydrochlorid (Mictonorm®) bei der Ratte. Pharmazie, 43, 96–98.
Hüller G., Haustein K.O., Scheithauer S. (1988): Studies on the metabolic pattern of propiverine in urine after single administration. Pharmazie, 43, 91–95.
Wengler A., Schneider T., Zschiesche M., Siegmund W. (1988): Untersuchungen zum Metabolismus des Blasenspasmolytikums Propiverin (Mictonorm®) beim Menschen. Pharmazie, 43, 652–653.
Wengler A., Siegmund W. Klebingat K.J., Schutz M., Kaliwe E. (1989): Metabolismus von Propiverin in adulten und fetalen Humanlebermikrosomen. Z. Klin. Med., 44, 221–224.
Wengler A. (1989): Untersuchungen zum In-vitro-Metabolismus des Blasenspasmolytikums Propiverin (Mictonorm®) bei Mensch und Ratte. Dissertation, University of Greifswald.
Brosen K. (1990): Recent developments in hepatic drug oxidation. Implications for clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 18, 220–239.
Eichelbaum M., Gross A.S. (1990): The genetic polymorphism of debrisoquine/sparteine metabolism — clinical aspects. Pharmacol. Ther., 46, 377–394.
Meyer U.A., Skoda R.C., Zanger U.M. (1990): The genetic polymorphism of debrisoquine/sparteine metabolism — molecular mechanisms. Pharmacol. Ther., 46, 297–308.
Lennard M.S. (1990): Genetic polymorphism of sparteine/debrisoquine oxidation: A reappraisal. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 67, 273–283.
Siegmund W., Hanke W., Zschiesche M., Franke G., Biebler K.E., Wilke A. (1990): N-acetylation and debrisoquine type oxidation polymorphism in Caucasians — with reference to age and sex. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol., 28, 504–509.
Leydhecker and Kriegelstein (1981): Untersuchungsmethoden des Auges. Leipzig, Thieme.
Enfors B. (1962): Parotid and submandibular secretion in man. Acta Otolaryngol., 275 suppl.
Aaltonen L., Kanto J., Iisalo E., Pihlajamäki K. (1984): Comparison of radioreceptor assay and radioimmunoassay for atropine. Pharmacokinetic application. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 26, 613–617.
Kaila T., Ali-Melkkilä T., Iisalo E., Kanto J. (1990): Radioreceptor assay for pharmacokinetic studies of glycopyrrolate. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 67, 313–316.
Williams L.T., Lefkowitz R.J. (1978): Receptor binding studies in adrenergic pharmacology, New York, Raven, pp. 27–41.
Sachs L. (1988): Statistische Methoden: Planung und Auswertung. Berlin, Springer.
Kentala E., Kaila T., Iisalo E., Kanto J. (1990): Intramuscular atropine in healthy volunteers: a pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol., 28, 399–404.
Lahdes K., Kaila T., Huupponen R., Salminen L., Iisalo E. (1988): Systemic absorption of topically applied ocular atropine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 44, 310–314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, C., Siegmund, W., Huupponen, R. et al. Kinetics of propiverine as assessed by radioreceptor assay in poor and extensive metabolizers of debrisoquine. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 18, 265–272 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03188807
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03188807