Abstract
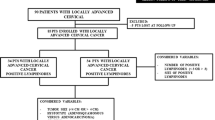
Objective: To investigate the effect of adjuvant chemotherapy on early stage cervical cancer with bulky tumor. Methods: Between Mar 1998 and Aug 2002, 162 patients of cervical cancer with Ib∼IIa stage were investigated. 21 patients with bulky tumors (>-4cm) were managed by cisplatin-based chemotherapy followed by radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy (Bulky-chemo group, BC group). The change of tumor size, the depth of stromal invasion, lymph node metastasis and the involvement of surgical specimens were assessed after operation and compared with those in 57 patients with bulky tumors (Bulky-nonchemo group, BN group) and 84 patients with the tumor size less than 4cm (small group, S group) who underwent surgery as the first step of treatment. Chemotherapy with the same regimen was offered for another 1∼2 cycles after operation and the survival situation was followed up. Results: The tumor size of 21 patients in BC group were decreased to varying degrees after chemotherapy, 15 patients were shown as clinical effectiveness (71.43%). And the blood loss during operation (352.35+-19.01ml) was significantly lower than that in BN group (619.05+-35.58ml), t=4.37) and that in S group (568.07+-45.23ml, t=3.36) patients. The incidence of lymph node metastasis (9/78) in patients with bulky tumors was greatly higher than those with tumor size less than 4cm (3/84, X2=4.416); its prevalence rate of deep wall infiltration (8/78) was also higher than that of the latter group (2/84), while with no statistical significance (X2=3.089). Histology showed that there was no case of marginal involvement in all patients. The ratio of both deep stromal invasion (1/21) and positive lymph node (2/21) in BC group was lower than that in BN group (7/57, 7/57 respectively), but neither with statistical significance (X2=0.0103 and 0.8193 respectively). Conclusion: Pre-operative chemotherapy can improve decreasing the primary tumor size and facilitate the following radical surgery. While the effect of adjuvant chemotherapy on subclinical lymph vascular involvement control and in turn its long-term effect on the improvement of relapse-free survival should be further testified.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Burghardt E, Pickel H. Local spread and lymph node involvement in cervical cancer[J]. Obstet Gynecol 1978; 52: 138–45.
Chung CK, Nahhas WA, Stryker JA, et al. Analysis of factors contributing to treatment failures in stages IB and IIA carcinoma of the cervix[J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1980; 138: 550–6.
Alvarez RD, Soong SJ, Kinney WK, et al. Identification of prognostic factors and risk groups in patients found to have nodal metastasis at the time of radical hysterectomy for early-stage squamous carcinoma of the cervix[J]. Gynecol Oncol 1989; 35: 130–5.
Micheletti E, La Face B, Bianchi E. Continuous infusion of carboplatin during conventional radiotherapy treatment in advanced squamous carcinoma of the cervix uteri IIB-IIIB (UICC). A phase I/II and pharmacokinetic study [J]. Am J Clin Oncol 1997; 20: 613–20.
Horn LC, Fischer U, Bilek K. Histopathological prognostic factors in primary surgically teated cervix carcinoma[J]. Zentralbl Gynakol 2001; 123: 266–74.
Scheungraber C, Muller B, Kohler C, et al. Detection of disseminated tumor cells in patients with cervical cancer[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2002; 128: 329–35.
Perez CA, Grigsby PW, Chao KS, et al. Tumor size, irradiation dose, and long-term outcome of carcinoma of uterine cervix[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1998; 41:307–17.
Adachi S, ogasawara T, Tsubamoto H, et al. Intravenous nedaplatin and intraarterial cisplatin with transcatheter arterial embolization for patients with locally advanced uterine cervical cancer[J]. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 2001; 21: 105–10.
Dowdy SC, Boardman CH, Wilson TO, et al. Multimodal therapy including neoadjuvant methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin (MVAC) for stage IIB to IV cervical cancer[J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002; 186: 1167–73.
Duenas-Gonzalez A, Lopez-Graniel CM, Mota A, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by surgery in locally advanced cervical carcinoma[J]. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 2908–9.
Chen CA, Cheng WF, Wei LH, et al. Radical hysterectomy alone or combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the treatment of early stage bulky cervical carcinoma[J]. J Formos Med Assoc 2002; 101: 195–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Biography: LING Hu-hua(1969–), female, master of medicine, lecturer, Chongqing University of Medical Scinece, majors in gynecological oncology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linghu, H., Xu, Xr., Mei, Yy. et al. Short-time analysis for adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early-stage bulky cervical carcinoma. Chin J Cancer Res 15, 144–148 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974920
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974920