Abstract
Background
Angiogenesis plays an important role in the growth and metastasis of solid tumors. Several angiogenic factors have been identified, and thymidine phosphorylase (TP) is thought to be one such factor. To date, little information is available on the relationship between TP and other clinicopathological variables.
Methods
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded materials from 116 primary breast carcinomas were used. The expression of TP, estrogen receptor, Bcl-2, Bax, p53, c-erbB-2 and MIB-1 was examined by immunohistochemical methods.
Results
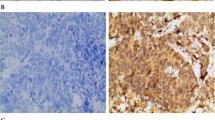
Nuclear and/or cytoplasmic TP expression was observed in the neoplastic cells, and accentuation of TP was often present at the infiltrating tumor edge and intraductal spread region. Tumor cell TP expression was significantly inversely correlated with histological grade (p<0.05) and positively correlated with Bcl-2 expression, but no association with other tumor variables was found.
Conclusions
TP is associated with Bcl-2 expression and tumor differentiation in breast cancer. TP may be a new prognostic parameter for breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TP:
-
Thymidine phosphorylase
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- EIC:
-
Extensive intraductal component
- 5-FU:
-
5-flurouracil
- MTX:
-
Methotrexate
References
Blood CH, Zetter BR: Tumor interactions with the vasculature; Angiogenesis and tumor metastasis.Biochim Biophys Acta 1032:89–118, 1990.
Furukawa T, Yoshimura A, Sumizawa T,et al: Angiogenic factor.Nature. 356:668, 1992.
Finnis C, Dodsworth N, Pollitt CE,et al: Thymidine phosphorylase activity of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor is responsible for endothelial cell mitogenicity.Eur J Biochem 212:201–210, 1993.
Maeda K, Chung YS, Ogawa Y,et al: Thymidine phosphorylase/platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor expression associated with hepatic metastasis in gastric carcinoma.Br J Cancer 73:884–888, 1996.
O’Brien T, Cranston D, Fuggle S,et al: Different angiogenic pathways characterize superficial and invasive bladder cancer.Cancer Res 55:510–513, 1995.
Reynolds K, Farzanch F, Collins WP,et al: Association of ovarian malignancy with expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor.J Natl Cancer Inst 86:1234–1238, 1994.
Saeki T, Takashima S, Hosokawa S,et al: Differential expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor (thymidine phosphorylase) in nonpolypoid and polypoid lesions of the colon.Int J Oncol 8:1105–1111, 1996.
Engels K, Fox SB, Whitehouse RM,et al: Up-regulation of thymidine phosphorylase expression is associated with a discrete pattern of angiogenesis in ductal carcinomasin situ of the breast.J Pathol 182:414–420, 1997.
Fox SB, Westwood M, Moghaddam A,et al: The angiogenic factor platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase is up-regulated in breast cancer epithelium and endothelium.Br J Cancer73:275–280, 1996.
Toi M, Hoshina S, Taniguchi T,et al: Expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase in human breast cancer.Int J Cancer 64:79–82, 1995.
WHO: Histological Ty** of Breast Tumors, 2nd ed, International HistologicalClassification of Tumors, No.2, World Health Organization, Geneva, 1981.
Bloom HJR, Richardson WW: Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer.Br J Cancer 11:359–377, 1957.
Boyages J, Recht A, Connolly JL,et al: Early breast cancer: Predictors of breast recurrence for patients treated with conservative surgery and radiation therapy.Radiother Oncol 19:29–41, 1990.
Yonenaga F, Takashi T, Ohi Y,et al: The expression of thymidine phosphorylase/platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor is correlated to angiogenesis in breast cancer.Pathol Int 48:850–856, 1998.
Eda H, Fujimoto K, Watanabe S,et al: Cytokines induce thymidine phosphorylase expression in tumor-cells and make them more susceptible to 5’-deoxy-5-fluorouridine.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 32:333–338, 1993.
Griffiths L, Dachs GU, Bicknell R,et al: The influence of oxygen tension and pH on the expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase in human breast tumor cells grownin vitro andin vivo.Cancer Res 57:570–572, 1997.
Ishikawa F, Miyazono K, Hellman U,et al: Identification of angiogenic activity and the cloning and expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor.Nature 338:557–562, 1989.
Leek RD, Landers R, Fox SB,et al: Association of tumor necrosis factor alpha and its receptors with thymidine phosphorylase expression in invasive breast carcinoma.Br J Cancer 77:2246–2251, 1998.
WUJ: Apoptosis and angiogenesis: Two promising tumor markers in breast cancer.Anticancer Res 16:2233–2239, 1996.
Zhang GJ, Kimijima I, Abe R,et al: Apoptotic index correlates to bcl-2 and p53 protein expression, histological grade and prognosis in invasive breast cancers.Anticancer Res 18:1989–1998, 1998.
Gee JM, Robertson JF, Ellis IO,et al: Immuno-cytochemical localization of bcl-2 protein in human breast cancers and its relationship to a series of prognostic markers and response to endocrine therapy.Int J Cancer 59:619–628, 1994.
Huang Y, Ray S, Reed JC,et al: Estrogen increases intracellular p26Bcl-2 to p21Bax ratios and inhibits taxol-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat 42:73–81, 1997.
Iltzsch MH, El Kouni MH, Cha S: Kinetic studies of thymidine phosphorylase from mouse liver.Biochemistry 24:6799–6807, 1985.
Haber M, Madafiglio J, Norris MD: Methotrexate cytotoxicity determination using the MTT assay following enzymatic depletion of thymidine and hypoxanthine.J Cancer Res Clin oncol 119:315–317, 1993.
Patterson A, Zhang H, Moghaddam A,et al: Increased sensitivity to the pro-drug 5’-deoxy-5-fluorouridine and modulation of 5-fluoro-2’-deoxyuridine sensitivity in MCF-7 cell transfected with thymidine phosphorylase.Br J Cancer 72:669–675, 1995.
Touboul E, Buffat L, Belkacemi Y,et al: Local recurrences and distant metastases after breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy for early breast cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43:25–38, 1999.
Sjostrom J, Krajewski S, Franssila K,et al: A multivariate analysis of tumour biological factors predicting response to cytotoxic treatment in advanced breast cancer.Br J Cancer 78:812–815, 1998.
Pinder SE, Murray S, Ellis IO,et al: The importance of the histologic grade of invasive breast carcinoma and response to chemotherapy.Cancer 83:1529–1539, 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Sakurai, T., Shan, L. et al. Thymidine phosphorylase expression correlates with tumor differentiation and bcl-2 in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer 7, 210–214 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02967462
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02967462