Abstract
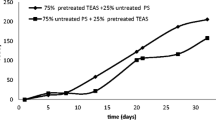
In order to enhance the degradation efficiency of waste activated sludge (WAS) by thermophilic aerobic digestion, an ultrasonic pretreatment was examined. It was observed that ultrasonic pretreatment increased the solubilization of organic matter in the WAS and that the solubilization ratio of the organics increased during the first 30 min but did not extensively increase thereafter. Therefore, a pretreatment time of 30 min was determined to be the economical pretreatment time from the experimental results. From the digestion experiments, which was conducted using the WAS collected from an oil refinery plant in Inchon, Korea, investigating the effects of an ultrasonic pretreatment on thermophilic aerobic digestion, it was confirmed that the proposed ultrasonic pretreatment was effective at enhancing the release of the cellular components in WAS and the degradation of released components in the thermophilic aerobic digestion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rocher, M., G. Goma, A. Pilas Begue, L. Louvel, and J. L. Rols (1999) Toward a reduction in excess sludge production in activated sludge process: Biomass physiochemical treatment and biodegradation.Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 51: 883–890.
Häner, A., C. A. Mason, and G. Hamer (1994) Aerobic thermophilic waste sludge biotreatment: Carboxylic acid production and utilization during biodegradation of bacterial cells under oxygen limitation.Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 40: 904–909.
Mason, C. A., A. Häner, and G. Hamer (1992) Aerobic thermophilic waste sludge treatment.Wat. Sci. Tech. 25(1): 113–118.
Hamer, G. and H. P. Zwiefelhofer (1986) Acrobic thermophilic hygienisation: A supplement to anaerobic mesophilic waste sludge digestion.Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 64: 417–424.
Bomio, M., B. Sonnleitner, and A. Fiechter (1989) Growth and biocatalytic activities of aerobic thermophilic populations in sewage sludge.Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32: 356–362.
Mason, C. A., G. Hamer, T. Fleischmann, and C. Lang (1987) Aerobic thermophilic biodegradation of microbial cells.Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25: 568–573.
Baier, U. and H. P. Zwiefelhofer (1991) Effects of aerobic thermophilic pretreatment.Wat. Sci. Technol. 23: 56–63.
Pagilla, K. R., K. C. Craney, and W. H. Kido (1996) Aerobic thermophilic pretreatment of mixed sludge for pathogen reduction andNorcardia control.Water Envir. Res. 68: 1093–1098.
Kim, Y. K., Y. S. Eom, W. H. Lee, and J. W. Choi (2000) The development of thermophilic aerobic sludge digestion process for industrial wastewater treatment plant. In:Proceedings of Ist World Water Congress of the International Water Association. July 3–7. Paris, France.
Wang, O. H., J. C. Chen, K. Kakimoto, H. I. Ogawa, and Y. Kato (1995) Pretreatment of waste activated sludge results in enhancement of its anaerobic digestion efficiency.J. Soc. Wat. Environ. (Japan). 19: 875–882.
Wang, Q., M. Kuninobu, K. Kakimoto, H. I. Ogawa, and Y. Kato (1999) Upgrading of anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge by ultrasonic pretreatment.Bioresource Technol. 68: 309–313.
Bradford, M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microorganism quatities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Dubois, M., K. A. Gilles, J. K. Hamilton, P. A. Rebers, and F. Smith (1956) Calorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances.Anal. Chem. 28: 350–356.
Häner, A., C. A. Mason, and G. Hamer (1994) Death and lysis during aerobic thermophilic sludge treatment: characterization of recalcitranted products.Wat. Res. 28: 863–869.
Kume, S. and Y. Fujio (1990) Digestion of municipal sewage sludge by a mixture of thermophilicBacilli and their culture extract.J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 36: 189–194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YK., Kwak, MS., Lee, W.H. et al. Ultrasonic pretreatment for thermophilic aerobic digestion in industrial waste activated sludge treatment. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 5, 469–474 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931950
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931950