Abstract
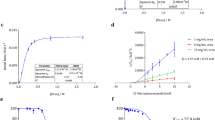
Twenty six urea analogues, most of which have already been approved for human use, were tested for their antiurease activityin vitro. Cell-free extracts obtained from a clinical isolate ofProteus mirabilis was used as the source of enzyme. Acetohydroxamic acid which is a proven potent urease inhibitor but not approved for human use was again shown to be the most active compound among the tested. Phenacemide, cycloserine, and deferoxamine were demonstrated to be moderate inhibitors. Oxytetracycline, trimethoprim and cefamandole revealed a demonstrable antiruease activity, but only at very high concentrations.
The antiurease activity of cycloserine, trimethoprim, and cefamandole was pH dependent; only active at acidic pH. The inhibitory activity of acetohydroxamic acid however was independent of change in pH. Hydrogen ion concentration plays an important role in urease activity and acidification (pH 5.5) alone eliminates approximately 65% of the enzymic activity. Adjustment of pH therefore appears to be an important adjunct in reducing urease activity and should always be studied to maximize the efficacy of antiurease compounds under investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Belding, M.E. and Kern, F. Jr.: Inhibition of urease by oxyteracycline.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 61: 560–566 (1963).
Burr, R.G.: Inhibition of urease by miscellaneous ions and compounds: Implications for the therapy of infection-induced urolithiasis.Invest. Urol. 15: 180–182 (1977).
Byrne, E. and Power, T.: Determination of ammonium nitrogen in animal slurries by an ammonia electrode.Commun. Soil. Plant Anal. 5: 51–65 (1974).
Conn, H.O., Leevy, C.M., Vlachcevic, Z.R., Rodgers, J.B., Maddrey, W.C., Seeff, L. and Levy, L.L.: Comparison of lactulose and neomycin in the treatment of chronic portalsystemic encephalopathy: A double blind controlled trial.Gastroenterology 72: 573–583 (1977).
Everett, G.M. and Richards, R.K.: Pharmacological studies of phenacetylurea (phenurone) and anticonvulsant drugs.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 106: 303–313 (1952).
Fishbein, W.N. and Carbone, P.P.: Urease catalysis II. Inhibition of the enzyme by hydroxyurea, hydroxylamine, and acetohydroxamic acid.J. Biol. Chem. 240: 2407–2413 (1965).
Griffith, D.P. and Musher, D.M.: Prevention of infected urinary stones by urease inhibition.Invest. Urol. 11: 228–233 (1973).
Kobashi, K., Hase, J. and Uehara, K.: Specific inhibition of urease by hydroxamic acids.Biochem. Biophys. Acta 65: 380–383 (1962).
Kunin, C.M.: “Detection, Prevention and Management of Urinary Tract Infection”, 3rd ed., 1979 p. 301–302. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia.
Lineweaver, H. and Burk, D.: The determination of enzyme dissociation constants.J. Am. Chem. Soc.,56: 658–666 (1934).
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265–275 (1951).
Rosenstein, I.J., Hamilton-Miller, J.M. and Brumfitt, W.: Role of urease in the formation of infection stones. Comparison of ureases from different sources.Infect. Immun. 32: 32–37 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, P.S., Suh, B., Strockbine, N.A. et al. In vitro inhibitory activities of urea analogues on bacterial urease. Arch. Pharm. Res. 9, 163–167 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02900001
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02900001