Abstract
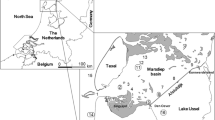
Study of horizontal and vertical distributions of the N/P (nitrogen versus phosphate) atom ratio in the northern South Yellow Sea showed that the ratio varied greatly in upper waters of the investigated area and was always much greater than the theoretical Redfield ratio of 16∶1 found below the themocline zone. It was in general higher near the coast and lower in the central part. With increasing depth, the ratio became smaller and smaller. This distribution pattern is attributed to: 1) the anthropogenic influence of the surface N and P which makes the N/P ratio differ from the normal value: 2) the easy adsorption of P on particles hinders P transport to the central part: 3) below the themocline zone, the N and P mainly come from the remineralization of the sedimented phytoplankton residues which have almost the theoretical Redfield value and; 4) the existence of the Yellow Sea Bottom Cold Water which inhibits the vertical exchange of the water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butler, L. I., 1979. Nutrient balance in the western English Channel.Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 8: 195–197.
China Ocean Yearbook Redaction Committee, 1994. China Ocean Yearbook. China Ocean Press, Bei**g, 469 pp. (in Chinese)
Cui, H., Sun, B. Y., 1991. The buffer mechanism of phosphate concentration in estuarine waters.Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology 1: 77–84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GEOHAB, 1998. A Plan for Co-ordinated Scientific Research and Co-operation to Develop International Capabilities for Assessment, Prediction and Mitigation. Report from a Joint IOC/SCOR Workshop. Havreholm, Denmark, 13–17 October 1998, 49 pp.
Gu, H. K., 1991. Marine Chemistry of the bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Science Press, Bei**g, 500 pp. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guo, W. D., Zhang, X. M., Yang, Y. P. et al., 1998. The assessment of the potential eutrophic state in Chinese coastal water.journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait 17: 64–70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hong, G. H., Chung, C. S., Kang, D. J. et al., 1993. Synoptic distribution of nutrients and major biogeochemical provinces in the Yellow Sea.In: D. C. Kim & Y. S. Kim, ed. Proceedings of ISEE '93 Circum-Pacific International Symposium on Earth Environment, Pusan, 85–99.
Hu, M. H., Yang, Y. P., Xu, C. L. et al., 1989. The phosphate limitation of phytoplankton in the Changjiang Estuary.Acta Oceanologica Sinica 11: 439–443. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Karydis, M., Ignatiades, L., Moschopoulou, N., 1983. An index associated with nutrient eutrophication in the marine environment.estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 16: 339–344.
Lee, Y. C., Qin, Y. S., Liu, R. Y., 1998. Yellow Sca Atlas. Ho Yong Publishing Co., Seoul., Korea, 524pp.
NERDA, 1979. Oceanographic Handbook of the Neighbouring Seas of Korea, 3rd Ed., Fish. Res. Dev. Agency, Busan, Korea, 650pp.
Pang, I. C., Hyun, K. H., 1998. Seasonal Variation of Water Mass Distributions in the Eastern Yellow Sea and the Yellow Sea Warm Current.Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography 33: 41–52.
Peng, Y. H., 1990. Analysis of the nutrient status in the Hong Kong sea area.China South Sea Research and Development 2: 6–10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shen, Z. L., 1995. The variations of nutrients in Jiaozhou Bay.In: Dong J. H. and Jiao N. Z. ed., Chinese Academic Press, Be**g, Study on the Ecology of the Jiaozhou Bay. P. 47–52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Spencer, C. P., 1975. The micronutrient elements.Chem. Oceanogr. 2: 245–300.
Yan, T., Zhou, M. J., Zeng, C. K., 2000. Reviews of studies on toxic dinoflagellatePfiesteria piscicida.Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica 31(3): 110–116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang, Baodong, Wang, Guiyun, Chung chang-Soo et al., 1999. Horizontal distributions and transportation of nutrients in the southern Huanghai Sea.Acta Oceanologica Sinica 21 (6): 124–129. (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 4366 from Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Project 39790110 supported by NSFC, and also supported by MDMAF, KOICA and WSFRI in Korea and the SEPA, and IOCAS in China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rong-gen, L., Yoon, W.D., **g-yang, W. et al. The N/P ratio in the Northern South Yellow Sea in autumn. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 20, 384–388 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02847931
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02847931