Summary
The pharmacokinetics and urinary metabolite pattern of a single oral dose of chlorpropamide 250 mg have been studied in 6 extensive and 5 poor metabolizers of debrisoquine. Ammonium chloride was given orally to acidify the urine in order to make elimination of the parent drug dependent on metabolism alone.
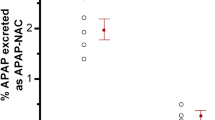
The concentration profile in serum and the pharmacokinetic parameters of the parent drug were similar in both groups. However, the ratio in urine of unchanged chlorpropamide to its hydroxylated metabolites was higher in poor than in extensive metabolizers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mahgoub A, Dring LG, Idle JR, Lancaster R, Smith RL (1977) Polymorphic hydroxylation of debrisoquine in man. Lancet II: 584–586
Gonzalez FJ, Skoda RC, Kimura S, Umeno M, Zanger UM, Nebert DW, Gelboin HV, Hardwick JR Meyer UA (1988) Char- acterization of common genetic defect in humans deficient in de- brisoquine metabolism. Nature 331:442–446
Jacqz E, Hall SD, Branch RA (1986) Genetically determined polymorphisms in drug oxidation. Hepatology 6:1020–1032
Kalow W (1987) Genetic variation in the human hepatic cyto- chrome P-450 system. Eur J Clin Pharmaco1 31:633–641
Huupponen R, Lammintausta R (1981) Chlorpropamide bioavailability and pharmacokinetics. Int J Clin Pharmacol 19: 331–333
Huupponen R, Viikari J, Saarimaa H (1982) Chlorpropamide and glibenclamide serum concentrations in hospitalized patients. Ann Clin Res 14:119–122
Bergman U, Christenson I, Jansson B, Wiholm B-E, Ostman J (1980) Wide variation in serum chlorpropamide concentration in outpatients. Eur J Clin Pharmaco1 18:165–169
Neuvonen PJ, Kärkkäinen S (1983) Effects of charcoal, sodium bicarbonate, and ammonium chloride on chlorpropamide kine- tics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 33:386–393
Brotherton PM, Grieveson P, McMartin C (1969) A study of me- tabolic fate of chlorpropamide in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 10: 505–514
Taylor JA (1972) Pharmacokinetics and biotransformation of chlorpropamide in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 13:710–718
Hill RE, Crechiolo J (1978) Determination of serum tolbuta- mide and chlorpropamide by high-performance liquid chroma- tography. J Chromatogr 145:165–168
Braselton WE, Jr, Ashline HC, Bransome ED, Jr (1975) Forma- tion of thermally stable derivatives for determination of tolbuta- mide and chlorpropamide by gas chromatography. Anal Lett 8: 301–313
Lewitt MJ (1973) Rapid methylation of micro amounts of nonvo- latile acids. Anal Chem 45:618–620
Braselton WE, Jr, Bransome ED, Huff TA (1977) Measurement of antidiabetic sulfonylureas in serum by gas chromatography with electron-capture detection. Diabetes 26:50–57
Braselton WE, Bransome ED, Jr, Huff TA (1982) Chlorpropa- mide metabolites in serum. Diabetes Care 5:348
Miners JO, Smith KJ, Robson RA, McManus ME, Veronese ME, Birkett DJ (1988) Tolbutamide hydroxylation by human liver microsomes, kinetic characterisation and relationship to other cytochrome P-450 dependent xenobiotic oxidations. Biochem Pharmaco1 37:1137–1144
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kallio, J., Huupponen, R. & Pyykkö, K. The relationship between debrisoquine oxidation phenotype and the pharmacokinetics of chlorpropamide . Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39, 93–95 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02657068
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02657068