Abstract
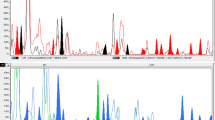
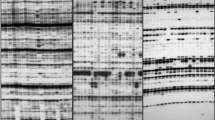
Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP) markers were successfully employed to analyze 15Artemia species and strains for genetic diversity. AFLP markers are extremely sensitive to even a small sequence variation. They are stable and more polymorphic than RAPD. Twelve pairs of primer combinations were used to detect AFLP bands, of which 384 were polymorphic, and DNA fingerprintings were obtained by using silver staining. The polymorphism analysis leads us to the following conclusions: 1.Artemia tibetiana seems to differentiate fromA. sinica. 2. The parthenogenetic populations from inland salt lakes could follow an evolutionary path that is different from that of the coastal parthenogenetic populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abatzopoulos, T.J., Zhang, B. and Sorgeloos, P. 1998.Artemia tibetiana: Preliminary characterization of a newArtemia species found in Tibet (People's Republic of China). International Study onArtemia. LIX. International Journal of Salt Lake Research 7: 41–44.
Abreu-Grobois, F.A. and Beardmore, J.A. 1980. International study onArtemia: II. Genetic characterization ofArtemia populations — an electrophoretic approach. In: G. Persoone, P. Sorgeloos, O. Roels and E. Jaspers (eds) The Brine ShrimpArtemia. Vol. 1: Morphology, Genetics, Radiobiology, Toxicology, pp. 133–146. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium.
Abreu-Grobois, F.A. and Beardmore, J.A. 1982. Genetic differentiation and speciation in the brine shrimpArtemia. In: C. Barigozzi (eds) Mechanisms of Speciation, pp. 345–376. Alan R. Liss, New York.
Badaracco, G., Baratelli, L., Ginelli, E., Meneveri, R., Plevani, P., Valsasnini, P. and Barigozzi, C. 1987. Variation in repetitive DNA and heterochromatin in the genusArtemia. Chromosoma 95: 71–75.
Badaracco, G., Tubiello, G., Benfante, R., Cotelli, F., Maiorano, D. and Landsberger, N. 1991. Highly repetitive DNA sequence in parthenogeneticArtemia. Journal of Molecular Evolution 32: 31–36.
Badaracco, G., Bellorini, M. and Landsberger, N. 1995. Phylogenetic study of bisexualArtemia using random amplified polymorphic DNA. Journal of Molecular Evolution 41: 150–154.
Barigozzi, C., Badaracco, G., Plevani, P., Baratelli, L., Profeta, S., Gienlli, E. and Meneveri, R. 1984. Heterochromatin in the genusArtemia. Chromosoma 90: 332–337.
Cai, Y. 1989. A redescription of the brine shrimp (Artemia sinica). The Wasman Journal of Biology 47: 105–110.
Cruces, J., Wonenburger, M.L.G., Diaz-Guerra, M., Sebastin, J. and Renart, J. 1986. Satellite DNA in the crustaceanArtemia. Gene 44: 341–345.
Gao, M.J., Ge, L. and Cai, Y.N.. 1994. Isoenzyme analysis on the relationships between parthenogenetic and bisexualArtemia from China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 16(5): 92–98 [in Chinese]
Günther, R.T. 1890. Crustacea. In: R.T. Günther (ed.) Contributions to the Natural History of Lake Urmia. N.W. Persia and Its Neighborhood, Vol. 27, pp. 394–398. Journal of Linnaeus Society (Zoology).
Kellogg, V.A. 1906. A newArtemia and its life conditions. Science 24: 594–596.
Lansberger, N., Cancelli, S., Carettoni, D., Barigozzi, C. and Badaracco, G. 1992. Nucleotide varition and molecular structure of the heterochromatic repetitiveAlu I DNA in the brine shrimpArtemia franciscana. Journal of Molecular Evolution 35: 486–491.
Lenz, P. 1980. Ecology of an alkali-adapted variety ofArtemia from Mono lake, California, USA. In: G. Persoone, P. Sorgeloos, O. Roels and E. Jaspers (eds) The Brine ShrimpArtemia, Vol. 3: Ecology, Culturing, Use in Aquaculture, pp. 79–96. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium.
Perez, M.L., Valverda, J.R., Batuecas, B., Amat, F., Marco, R. and Garrese, R. 1994. Speciation in theArtemia genus; Mitochondrial DNA analysis of bisexual and parthenogenetic brine shrimps. Journal of Molecular Evolution 38: 156–168.
Piccinelli, M. and Prosdocimi, T. 1968. Descrizione tassonomica delle due speciesArtemia salina L. eArtemia persimilis n. sp. Rc Ist Iomb Sci Lett B 102: 170–179.
Pilla, E.J.S. and Beardmore, J.A. 1994. Genetic and morphometric differentiation in Old World bisexual species ofArtemia (the brine shrimp). Heredity 73: 47–56.
Sun, Y., Zhong, Y.C., Song, W.Q., Zhang, R.S., Chen, R.Y. and Sorgeloos, P. 1999. Detection of genetic relationships among fourArtemia species using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) International Journal of Salt Lake Research 8(2): 139–147.
Triantaphyllidis, G.V., Griel, G.R.T., Abatzopoulos, T.J., Thomas, K.M., Peleman, J., Beardmore, J.A. and Sorgeloos, P. 1997. International study onArtemia. LVII. Morphological and molecular characters suggest conspecificity of all bisexual European and North AfricanArtemia populations. Marine Biology 129: 477–478.
Vos, P., Hogers, R., Bleeker, M., Reijans, M., Van De Leet, T., Hornes, M. Fijters, A., Pot, J., Peleman, J., Kuiper, M. and Zabeau, M. 1995. AFLP: A new technique for DNA fringerprinting. Nucleic Acids Research 23: 4407–4414.
Zabeau, M. and Vos, P. 1993. Selective restriction fragment amplifications: a general method for DNA fingerpriting. European Patent Application of 92402629 (Pub 1. No. 0534 858 A1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Song, WQ., Zhong, YC. et al. Diversity and genetic differentiation inArtemia species and populations detected by AFLP markers. International Journal of Salt Lake Research 8, 341–350 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442119
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442119