Abstract
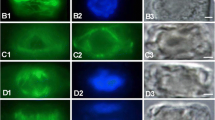
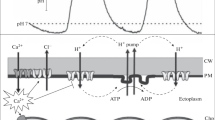
The freshwater algaChara corallina Klein ex Willd., em. R.D.W. (=C. australis R.Br.) develops alternating outward (acid) and inward (alkaline) current areas on its surface when illuminated. Exposure of cells to vinblastine, colchicine, or oryzalin caused a reduction in and a shifting of this extracellular current pattern. Removal of these agents from the bathing media resulted in regeneration of the initial current profile. Because these agents all affect tubulin, microtubules may be responsible for orchestrating the transmembrane currents responsible for the acid and alkaline banding phenomenon. Analysis of the membrane potential showed a fast depolarization after vinblastine exposure; however, analysis of the current-voltage curve did not show a change in membrane conductance. A 30-min colchicine treatment decreased the conductance of the plasma membrane with either an hyperor a depolarization in the membrane potential. In contrast, although a 9-h exposure to oryzalin caused a major reduction in the extra-cellular current pattern, only minor changes were observed in the membrane potential and conductance. However, in the presence of oryzalin, the time constants in the light response of the membrane potential increased over this 9-h period. Collectively, these results implicate an involvement of microtubules in spatial control of plasma-membrane transport events inC. corallina.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- I/V:
-
current voltage curve
- CPW/B:
-
artificialChara pond water
References
Bajer, A.S., Molé-Bajer, J. (1986) Drugs with colchicine-like effects that specifically disassemble plant but not animal microtubules. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.466, 767–784
Beilby, M.J. (1984) Current-voltage characteristics of the proton pump atChara plasmalemma. I. pH dependence. J. Membr. Biol.81, 113–125
Bernier-Valentin, F., Aunis, D., Rousset, B.J. (1983) Evidence for tubulin-binding sites on cellular membranes: plasma membranes, mitochondrial membranes, and secretory granule membranes. Cell Biol.97, 209–216
Fisahn, J., Lucas, W.J. (1990a) Application of asymmetric alternating voltage pulse series for investigation of the action potential inChara. Plant Cell Physiol.31, 155–157
Fisahn, J., Lucas, W.J. (1990b) Inversion of extracellular current and axial voltage profile inChara andNitella. J. Membr. Biol.113, 1–8
Fisahn, J., Mikschl, E., Hansen, U.-P. (1986a) Separate oscillations of the electrogenic pump and of a K+ channel inNitella as revealed by simultaneous measurement of membrane potential and of resistance. J. Exp. Bot.37, 34–47
Fisahn, J., Hansen, U.-P., Gradmann, D.J. (1986b) Determination of charge, stoichiometry and reaction constants from I/V curve studies on a K+ transporter inNitella. J. Membr. Biol.94, 245–252
Fisahn, J., McConnaughey, T., Lucas, W.J. (1989) Oscillations in extracellular current, external pH and membrane potential and conductance in the alkaline bands ofNitella andChara. J. Exp. Bot.40, 1185–1193
Gunning, B.E.S., Hardham, A.R. (1982) Microtubules. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.33, 651–698
Hansen, U.-P., Gradmann, D., Sanders, D., Slayman, C.L. (1981) Interpretation of current-voltage relationships for “active” ion transport systems: I. Steady-state reaction-kinetic analysis of class-I mechanisms. J. Membr. Biol.63, 165–190
Hashizume, T., Akiba, S., Sato, T., Fujii, T., Watanabe, S., Sasaki, J. (1988) Vinblastine inhibits platelet aggregation by a microtubule-independent mechanism, probably by its perturbing action on the plasma membrane. Thromb. Res.50, 181–190
Hucho, F., Hilgendorf, R. (1989) The selectivity filter of a ligandgated ion channel. The helix-M2 model of the ion channel of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. FEBS Lett.257, 17–23
Keifer, D.W., Lucas, W.J. (1982) Potassium channels inChara corallina: control and interaction with the electrogenic H+ pump. Plant Physiol.69, 781–788
Lloyd, C.W. (1987) The plant cytoskeleton: the impact of fluorescence microscopy. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.38, 119–139
Lucas, W.J. (1975) The influence of light intensity on the activation and operation of the hydroxyl efflux system ofChara corallina. J. Exp. Bot.26, 347–360
Lucas, W.J. (1982) Mechanism of acquisition of exogenous bicarbonate by internodal cells ofChara corallina. Planta156, 181–192
Lucas, W.J. (1983) Photosynthetic assimilation of exogenous HCO3/- by aquatic plants. Annu. Rev. Plant. Physiol.34, 71–104
Lucas, W.J., Nuccitelli, R. (1980) HCO3/- and OH- transport across the plasmalemma ofChara corallina: spatial resolution obtained using extracellular vibrating probe. Planta150, 120–131
Lucas, W.J., Spanswick, R.M., Dainty, J. (1978) HCO3/- influx across the plasmalemma ofChara corallina: physiological and biophysical influence of 10 mM K+. Plant Physiol.61, 487–493
Luduena, R.F., Anderson, W.H., Prasad, V., Jordan, M.A., Ferrigni, K.C., Roach, M.C., Horowitz, P.M., Murphy, D.B., Fellous, A. (1986) Interactions of vinblastine and maytansine with tubulin. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.466, 718–732
Morejohn, L.C., Fosket, D.E. (1984) Taxol-induced rose microtubule polymerization in vitro and its inhibition by colchicine. J. Cell Biol.99, 141–147
Niggli, V., Burger, M.M. (1987) Interaction of the cytoskeleton with the plasma membrane. J. Membr. Biol.100, 97–121
Nuccitelli, R. (1986) A two-dimensional vibrating probe with a computerized graphics display. In: Ionic currents in development, pp. 13–20, Nuccitelli, R., ed. Liss, New York
Ribbi-Jaffe, A., Apitz-Castro, R. (1979) The effect of colchicine on human blood platelets under conditions of short-term incubation. Biochem. J.178, 449–454
Richmond, P.A. (1983) Patterns of cellulose microfibril deposition and rearrangement inNitella: in vivo analysis by a birefringence index. J. Appl. Polymer. Sci.: Applied Polymer Symp.37, 107–122
Robinson, D.G., Herzog, W. (1977) Structure, synthesis and orientation of microfibrils. III. A survey of the action of microtubule inhibitors on microtubules and microfibril orientation inOocystis solitaria. Cytobiologie15, 463–474
Spanswick, R.M. (1981) Electrogenic ion pumps. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.32, 267–289
Tyerman, S.D., Findlay, G.P., Paterson, G.J. (1986) Inward membrane current inChara inflata: Effects of pH, Cl--channel blockers and NH4/-, and significance for the hyperpolarized state. J. Membr. Biol.89, 153–161
Upadhyaya, M.K., Noodén, L.D. (1980) Mode of dinitroaniline herbicide action. II. Characterization of [14C]oryzalin uptake and binding. Plant Physiol.66, 1048–1052
Vassilev, P.M., Kanazirska, M.P., Tien, H.T. (1986) Microtubule-dependent membrane interactions studied in two types of double bilayer membrane systems. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg.15, 395–406
Weerdenburg, C., Seagull, R.W. (1988) The effects of taxol and colchicine on microtubule and microfibril arrays in elongating plant cells in culture. Can. J. Bot.66, 1707–1716
Williamson, R.F., Perkin, J.L., McCurdy, D.W., Craig, S., Hurley, U.A. (1986) Production and use of monoclonal antibodies to study the cytoskeleton and other components of the cortical cytoplasm ofChara. Eur. J. Cell Biol.41, 1–8
Zisapel, N., Levi, M., Gozes, I. (1980) Tubulin: an integral protein of mammalian synaptic vesicle membranes. J. Neurochem.34, 26–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by National Science Foundation grant DCB-88-16077.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fisahn, J., Lucas, W.J. Effects of microtubule agents on the spatial and electrical properties of the plasma membrane inChara corallina . Planta 182, 506–512 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02341025
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02341025