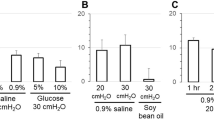
Summary
Active sodium transport was completely and irreversibly inhibited in toad urinary bladders photolyzed in the presence of iodeam loride.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.D. Bicking, J.W. Mason, O.W. Woltersdorf, Jr, J.H. Jones, S.F. Kwong, C.M. Robb, and E.J. Cragoe, Jr, J. Med. Chem.8, 638 (1965).
P.J. Bentley, J. Physiol.,195, 317 (1968).
A.W. Cuthbert, J. Physiol., Lond.228, 681 (1973).
D.J. Benos and L.J. Mandel, Science199, 1205 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cobb, M.H., Scott, W.N. Irreversible inhibition of sodium transport by the toad urinary bladder following photolysis of amiloride analogs. Experientia 37, 68–69 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01965574
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01965574