Summary
-
1.
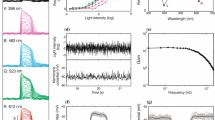
Random (white noise) fluctuations of both point and wide field light sources were presented to eyes of the fly,Calliphora stygia. At the same time, intracellular recordings were made from photoreceptor cells and from large monopolar cells (LMCs) in the lamina ganglionaris.
-
2.
Fourier analysis was used to determine the linear frequency response functions and coherence functions between the input light fluctuations and the resultant fluctuations in membrane potentials of the two types of cells.
-
3.
The frequency response function of the receptor-to-LMC pathway was estimated by dividing the overall light-to-LMC frequency response function by the light-to-receptor frequency response function. For small signal conditions this function is primarily a phase shift of 180° (inversion) and some increase in sensitivity with frequency.
-
4.
Comparison of results obtained with point and wide field stimuli did not reveal any significant differences between the frequency response functions of receptors or LMCs to either stimulus. No evidence of lateral interaction between receptors or LMCs was found.
-
5.
For a linear system the coherence function provides a measure of the signal-to-noise ratio as a function of frequency. Comparison of the coherence functions obtained from receptors and LMCs showed that there is no significant improvement or deterioration in the signal-to-noise ratio as the signal passes from receptors to LMCs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LMC:
-
large monopolar neuron
References
Autrum, H., Zettler, F., Järvilehto, M.: Postsynaptic potentials from a single monopolar neuron of the ganglion opticum 1 of the blowflyCalliphora. Z. verg. Physiol.70, 414–424 (1970)
Beastall, H.R.: White noise generator. Wireless World78, 127–128 (1972)
Bendat, J.S., Piersol, A.G.: Measurement and analysis of random data. New York: John Wiley 1966
Cajal, S.R., Sanchez, D.: Contribución al conocimiento de los centros nerviosos de los insectos. Parte 1. Rétina y centres ópticos. Trab. Lab. Invest. Biol. Univ. Madr.13, 1–168 (1915)
D'Azzo, J.J., Houpis, C.H.: Feedback control system analysis and synthesis. New York: McGraw-Hill 1966
Eckert, H., Bishop, L.G.: Nonlinear dynamic transfer characteristics of cells in the peripheral visual pathway of flies. Biol. Cybernetics17, 1–6 (1975)
French, A.S.: Automated spectral analysis of neurophysiological data using intermediate magnetic tape storage. Comp. Prog. Biomed.3, 45–57 (1973)
French, A.S., Järvilehto, M.: The dynamic behaviour of photoreceptor cells in the fly in response to random (white noise) stimulation at a range of temperatures. J. Physiol., in press (1978)
Horridge, G.A., Mimura, K., Hardie, R.C.: Fly photoreceptors III. Angular sensitivity as a function of wavelength and the limits of resolution. Proc. roy. Soc. LondonB194, 151–177 (1976)
Järvilehto, M., Zettler, F.: Localized intracellular potentials from pre- and post-synaptic components in the external plexiform layer of an insect retina. Z. vergl. Physiol.75, 422–440 (1971)
Järvilehto, M., Zettler, F.: Electrophysiological-histological studies on some functional properties of visual cells and second order neurons of an insect retina. Z. Zellforsch.136, 291–306 (1973)
Laughlin, S.B.: Neural integration in the first optic neuropile of dragonflies. I. Signal amplification in dark adapted second order neurons. J. comp. Physiol.84, 335–355 (1973)
Laughlin, S.B.: Neural integration in the first optic neuropile of dragonflies. III. The transfer of angular information. J. comp. Physiol.92, 377–396 (1974)
Laughlin, S.B.: Receptor and interneuron light-adaptation in the dragonfly visual system. Z. Naturforsch.30c, 306–308 (1975)
Laughlin, S.B.: Adaptations of the dragonfly retina for contrast detection and the elucidation of neural principals in the peripheral visual system. In: Neural principles in vision (ed. F. Zettler, R. Weiler), pp. 175–193. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976
McCann, G.D.: Nonlinear identification theory models for successive stages of visual nervous systems of flies. J. Neurophysiol.37, 869–895 (1974)
Mimura, K.: Some spatial properties in the first optic ganglion of the fly. J. comp. Physiol.105, 65–82 (1976)
Ratliff, F., Knight, B.W., Milkman, N.: Superposition of excitatory and inhibitory influences in the retina ofLimulus: Effect of delayed inhibition. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)67, 1558–1564 (1970)
Shaw, S.R.: Organization of the locust retina. Symp. zool. Soc. Lond.23, 135–163 (1968)
Shaw, S.R.: Retinal resistance barriers and electrical lateral inhibition. Nature (Lond.)255, 480–483 (1975)
Smola, U.: Voltage noise in insect visual cells. In: Neural principles in vision (ed. F. Zettler, R. Weiler), pp. 194–217. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976
Stein, R.B., French, A.S.: Models for the transmission of information by nerve cells. In: Excitatory synaptic processes (ed. P. Anderson, J.K.S. Jansen). Oslo: Universitets-forlaget 1970
Strausfeld, N.J., Campos-Ortega, J.A.: Vision in insects: Pathways underlying neural adaptation and lateral inhibition. Science195, 894–897 (1977)
Trujillo-Cenóz, O.: Some aspects of the structural organization of the intermediate retina of dipterans. J. Ultrastruct. Res.13, 1–33 (1965)
Zettler, F., Järvilehto, M.: Decrement-free conduction of graded potentials along the axon of a monopolar neuron. Z. vergl. Physiol.75, 402–421 (1971)
Zettler, F., Järvilehto, M.: Lateral inhibition in an insect eye. Z. vergl. Physiol.76, 233–244 (1972a)
Zettler, F., Järvilehto, M.: Intraaxonal visual responses from visual cells and second order neurons of an insect retina. In: Information processing in the visual systems of arthropods (ed. R. Wehner), pp. 217–222. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1972(b)
Zettler, F., Järvilehto, M.: Active and passive axonal propagation of non-spike signals in the retina ofCalliphora. J. comp. Physiol.85, 89–104 (1973)
Zettler, F., Weiler, F.: Neuronal processing in the first optic neuropile of the compound eye of the fly. In: Neural principles in vision (ed. F. Zettler, R. Weiler), pp. 227–237. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
On leave from: Department of Physiology, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta T6G 2H7, Canada
On leave from: Department of Physiology, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
We would like to express our gratitude to Dr. S. Laughlin and Dr. S. Shaw for their valuable assistance in preparing this manuscript. Support for this work was provided by the Medical Research Council of Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
French, A.S., Järvilehto, M. The transmission of information by first and second order neurons in the fly visual system. J. Comp. Physiol. 126, 87–96 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01342652
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01342652