Abstract
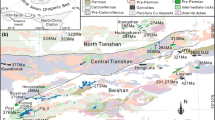
In closed magma systems SiO2 approximately measures differentiation progress and oxygen isotopes can seem to obey Rayleigh fractionation only as a consequence of the behaviour of SiO2. The main role of δ 18O is as a sensitive indicator of contamination, either at the start of differentiation (δ 18Oinit) or as a proportion of fractionation in AFC. Plots of δ 18O vs SiO2-allow to determine initial δ 18O values for different sequences for source comparison. For NBS-28=9.60, the δ 18O at 48% SiO2-varies between a high 6.4‰ for Kiglapait (Kalamarides 1984), 5.9‰ for Transhimalaya, 5.8‰ for Hachijo-Jima (Matsuhisa 1979), 5.6‰ for Koloula (Chivas et al. 1982) and a low 5.3‰ for the Darran Complex, New Zealand. The Transhimalayan batholiths (Gangdese belt) were emplaced in the ‘Ladakh-Lhasa terrane’, between the present-day Banggong-Nujiang, and Indus-Yarlung Tsangbo suture zones, after its accretion to Eurasia. The gradient of the least contaminated continuous (δ 18O vs SiO2-igneous trend line is similar to that of Koloula, and AFC calculations suggest a low secondary assimilation rate of less than 0.05 times the rate of crystallisation. Outliers enriched in 18O are frequent in the Lhasa, and apparently rare in the Ladakh transsect. Low-δ 18O (5.0‰−0‰) granitoids and andesites on the Lhasa-Yangbajain axis are the result of present day or recent near-surface geothermal activity; their quartzes still trace the granitoids to the Transhimalaya δ 18O trend line, but the distribution of low total rock or feldspar δ 18O values could be a guide to more recent heat flow and thermally marked tectonic lineaments. Two ignimbrites from Maqiang show hardly any 18O-contamination by crustal material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Academia Sinica (1980a) Geological Map of **zang (Tibet). Institute of Geology, Bei**g
Academia Sinica (1980b) Scientific Guidebook to South **zang (Tibet). Symposium on Qinghai-**zang Plateau. Bei**g, pp 104
Blattner P (1981) ‘Halogen geothermometry’ and case for post-Devonian granolite in Fiordland, New Zealand. Bull Mineral 104:811–816
Blattner P (1985) Isotope shift data and the natural evolution of geothermal systems. (WRI-4 Symposium) Chem Geol 49:187–203
Blattner P, Reid F (1982) The origin of lavas and ignimbrites of the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand, in the light of oxygen isotope data. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46:1417–1429
Blattner P, Dietrich V, Gansser A (1983) Contrasting 18O-enrichment and origins of High Himalayan and Transhimalayan intrusives. Earth Planet Sci Lett 65:276–286
Blattner P, Houston C (1986) Constant ‘oceanic’ oxygen isotope ratio of Taupo Volcanic Zone acidic magmas. Internat Volcanolog Congress New Zealand, Abstracts Vol, IAVCEI, p 4
Blattner P, Williams JG (1987) The Largs high latitude oxygen isotope anomaly and low initial δ 18O of the Darran Complex (New Zealand). Geol Soc NZ Ann Conf Dunedin Abstracts, p 16
Brandt SB (1974) Thermodynamics of isotope exchange in equilibrated mineral associations. Dokl Acad Nauk SSR (AGI transl) 2144:179–181
Chang Cheng-fa, Cheng Hsi-lan (1973) Some tectonic features of the Mt Chomolungma area, southern Tibet, China. Scientia Sinica 16:257–265
Chang Cheng-fa and 26 others (1986) Preliminary conclusions of the Royal Society and Academia Simica 1985 geotraverse of Tibet. Nature 323:501–507
Chivas AR, Andrew AS, Sinha AK, O'Neil JR (1982) Geochemistry of a Pliocene-Pleistocene oceanic-arc plutonic complex, Guadalcanal. Nature 300:139–143
Clayton RN, Mayeda TK (1963) The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotopic analysis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 27:43–52
Coulon C, Maluski H, Bollinger C, Wang S (1986) Mesozoic and Cenozoic volcanic rocks Tibet: 39Ar-40Ar dating, petrological characteristics and geodynamic significance. Earth Planet Sci Lett 79:281–302
Debon F, Le Fort P, Sheppard SMF, Sonet J (1986) The four plutonic belts of the Transhimalaya-Himalaya: a chemical, mineralogical, isotopic, and chronological synthesis along a Tibet-Nepal section. J Petrol 27:219–250
DePaolo D (1981) Trace element and isotopic effects on combined wallrock assimilation and fractional crystallisation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 53:189–202
DePaolo D (1985) Isotopic studies of processes in mafic magma chambers: I. The Kiglapait Intrusion, Labrador. J Petrol 26:925–951
Didier J (1973) Granites and their enclaves. Elsevier, Amsterdam New York, pp 393
France-Lanord C, LeFort P (1988) Crustal melting and granite genesis during the Himalayan collision orogenesis. Trans R Soc Edinburgh Earth Sci 79:183–195
Frank W, Gansser A, Trommsdorff V (1977) Geological observations in the Ladakh area. Schweiz Mineral Petrogr Mitt 57:89–113
Gansser A (1964) Geology of the Himalayas. Wiley, London, pp 289
Gansser A (1980a) The significance of the Himalayan suture zone. Tectonophysics 62:37–52
Gansser A (1980b) The division between Himalaya and Karakorum. Geol Bull Univ Peshawar 13:9–22
Gansser A (1981) The timing and significance of orogenic events in the Himalaya. In: Liu DS (ed) Geology, Geological History and Origin of Qinghai-**zang Plateau. Science Press, Bei**g, pp 23–28
Garlick GD (1966) Oxygen isotopic fractionation in igneous rocks, Earth Planet Sci Lett 1:361–368
Gonfiantini R (1984) Report on Advisory Group meeting on stable isotope reference samples for geochemical and hydrological investigations. Internat Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna
Harmon RS, Thorpe RS, Francis PW (1981) Petrogenesis of Andean andesites from combined O-Sr isotope relationships. Nature 290:396–399
Harmon RS, and 8 others (1984) Regionl O-, Sr-, and Pb-isotope relationships in late Cenozoic calc-alkaline lavas of the Andean Cordillera. J Geol Soc London 141:803–822
Harris NBW, Xu Rong-hua, Lewis CL, Hawkesworth CJ, Zhang Yuquan (in press) Isotope geochemistry of the Tibetan plateau
Hildreth W, Moorbath S (1988) Crustal contributions to arc magmatism in the Andes of Central Chile. Contrib Mineral Petrol 98:455–489
Hollister LS (1966) Garnet zoning: an interpretation based on the Rayleigh fractionation model. Science 154:1647–1649
Honegger K, Dietrich V, Frank W, Gansser A, Thöni M, Trommsdorff V (1982) Magmatism and metamorphism in the Ladakh Himalayas, Earth Planet Sci Lett 60:253–292
Isshiki N (1963) Petrology of Hachijo-Jima volcano group, Seven Izu Islands, Japan. Tokyo Univ Fac Sci J Set 2, 15:91–134
Ito E, Stern RJ (1986) Oxygen and strontium isotopic investigations of subduction zone volcanism: the case of the Volcano Arc and the Marianas Island Arc. Earth Planet Sci Lett 76:312–320
Ito E, White WM, Göpel C (1987) The O, Sr, Nd and Pb isotope geochemistry of MORB. Chem Geol 62:157–176
** Cheng-wei (1982) On the magmatism and island arc evolution of the Gangdese area, **zang. Res Geol Inst Geol, Academia Sinica (Bei**g) 49–54 (with Engl abstract)
** Cheng-wei, Zhou Yun-sheng (1978) Igneous rock belts in the Himalayas and the Gangdese arc and their genetic model. Scientia Geol Sinica 4:297–312
Kalamarides RI (1984) Kiglapait geochemistry VI: oxygen isotopes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1827–1836
Kalamarides RI (1986) High-temperature oxygen isotope fractionation among the phases of the Kiglapait intrusion, Labrador, Canada. Isotope Geosci 58:303–310
Kyser T, O'Neil JR, Carmichael ISE (1982) Genetic relationships among basic lavas and ultramatic modules: evidence from oxygen isotope compositions. Contri Mineral Petrol 81:88–102
Lassey KR, Blattner P (1988) Kinetically controlled oxygen isotope exchange between fluid and rock in one-dimensional advective flow. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:2169–2175
LeFort (1981) Manaslu leucogranite: a collision signature of the Himalaya. A model for its genesis and emplacement. J Geophys Res 86B:10545–68
Liao Zhi-jie, Guo Guo-ying, Liu Shi-bin (1980) Predevelopment study of Yangbajain geothermal field, **zang. Proc 2nd NZ Geothermal Workshop, Auckland pp 109–115
Matsuhisa Y (1979) Oxygen isotopic compositions of volcanic rocks from the East Japan island island arcs and their bearing on petrogenesis. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 5:271–296
Morse SA (1969) The Kiglapait layered intrusion, Labrador. Geol Soc Am Mem 112
Morse SA (1981) Kiglapait geochemistry IV: the major elements. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:461–479
Munksgaard NC (1984) High (δ 18O and possible pre-eruptional Rb-Sr isochrons in cordierite-bearing Neogene volcanics from SE Spain. Contrib Mineral Petrol 87:351–358
Neumann H, Mead J, Vitaliano CJ (1954) Trace element variation during fractional crystallisation as calculated from the distribution law. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 6:90–99
Notsu K, Isshiki N, Hirano M (1983) Comprehensive strontium isotope study of Quaternary volcanic rocks from the Izu-Ogasawara arc. Geochem J 17:289–302
Pichavant M, Montel JM (1988) Petrogenesis of a two-mica ignimbrite suite: the Macusani Volcanics, SE Peru. Trans R Soc Edinburgh Earth Sci 79:197–207
Powell C McA (1986) Continental underplating model for the rise of the Tibetan plateau. Earth Planet Sci Lett 81:79–94
Schärer U, Hamet J, Allegre CJ (1984) The Transhimalaya (Gangdese) Plutonism in the Ladakh region: a U-Pb and Rb-Sr study. Earth Planet Sci Lett 67:327–339
Schärer U, Xu Rong-Hua, Allegre CJ (1984) U-Pb geochronology of Gangdese (Transhimalaya) plutonism in the Lhasa-**gaze region, Tibet. Earth Planet Sci Lett 69:311–320
Sheppard SMF, Harris C (1985) Hydrogen and oxygen isotope geochemistry of Ascension Island lavas and granites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 91:74–81
Srimal N (1986) India-Asia collision: implications from the geology of the eastern Karakoram. Geology 14:523–527
Taylor HP Jr (1968) The oxygen isotope geochemistry of igenous rocks. Contrib Mineral Petrol 19:1–71
Taylor HP Jr, Epstein S (1962) Relationship between O18/O16 ratios in coexisting minerals of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Parts I and II. Geol Soc Am Bull 73:461–479 and 675–694
Wan Zi-yi, and seven others (1982) Tectonics of Yarlung Tsangbo suture zone **zang (Tibet). Guide to geological excursion. Geological Bureau of **zang, China, Lhasa, 24 pp
Weis D, Demaiffe D, Cauet S, Javoy M (1987) Sr, Nd, O and H isotopic ratios in Ascension Island lavas and plutonic inclusions; cogenetic origin. Earth Planet Sci Lett 82:255–268
Woodhead JD, Harmon RS, Fraser DG (1987) O, S, Sr, and Pb isotope variations in volcanic rocks from the northern Mariana Islands: implications for crustal recycling in intra-oceanic arcs. Earth Planet Sci Lett 83:39–52
Xu Rong-hua, ** Cheng-wei (1984) A geochronological study of the Quxu batholith, **zang. Scientia Geologica Sinica:414–422
Xu Rong-hua, Schärer U, Allegre CJ (1985) Magmatism and metamorphism in the Lhasa block (Tibet): a geochronological study. J Geol 93:41–57
Xu Yong (1988) Thesis, Dept of Geology, Bei**g University
Zhou Yun-sheng, ** Cheng-wei (1983) Plutonism and its tectonic environment in the Gangdese and Nyainqentanglha Mts of **zang, China. In: Shams FA (ed) Granites of Himalayas Karakorum and Hindukusch. Punjab Univ Lahore, pp 393–406
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blattner, P., Cheng-wei, J. & Yong, X. Oxygen isotopes in mantle related and geothermally altered magmatites of the Transhimalayan (Gangdese) ranges. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 101, 438–446 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00372217
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00372217