Summary
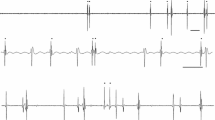
Primary endings of cat flexor muscle spindles supplied by fusimotor α-fibres respond to brief repetitive stimulation (20–250 Hz) of ventral root filaments with a train of discharges, which lasts as long as the duration of stimulation. Frequencies between 80 and 120 Hz increase the number of spindle discharges up to an average value of 50 Imp/sec. The most remarkable event is the shortening of intervals during the first 200–300 msec of repetitive stimulation. This effect is considered to be essential for indirect motor activation. The discharges of α-spindles are not silenced by tetanic contraction of extrafusal muscle fibres, provided that the contraction is either small or below the fusion frequency of the extrafusal muscle fibres.
Zusammenfassung
Die primären Afferenzen solcher Flexormuskelspindeln der Katze, die von fusimotorischen α-Fasern innerviert werden, beantworten die tetanische Reizung (20–250 Hz) der zugehörigen Ventralwurzelfilamente mit einer Entladungsfolge, die bei kurzen Serien etwa so lange wie die Reizdauer anhält. Der größte Brutto-Effekt wird mit 80–120 Hz erzielt und liegt im Mittel bei 50 Imp/sec. Auffällig ist die Verkürzung der Entladungsintervalle in den ersten 200–300 msec der repetierenden Reizung. Dieser Effekt könnte für die indirekte Aktivierung der Motorik von Bedeutung sein. Ein schwacher oder unverschmolzener extrafusaler Tetanus entlastet α-fusimotorisch aktivierte Flexormuskelspindeln nicht.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bessou, P., F. Emonet-Dénand, and Y. Laporte: Occurence of intrafusal muscle fibres innervation by branches of slow α motor fibres in the cat. Nature (Lond.) 198, 594–595 (1963).
— Motor fibres innervating extrafusal and intrafusal muscle fibres in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 180, 649–672 (1965).
Granit, R., H. D. Henatsch, and G. Steg: Tonic and phasic ventral horn cells differentiated by post-tetanic potentiation in cat extensors. Acta physiol. scand. 37, 114–126 (1956).
— C. G. Phillips, S. Skoglund, and G. Steg: Differentiation of tonic from phasic alpha ventral horn cells by stretch, pinna and crossed extensor reflexes. J. Neurophysiol. 20, 470–481 (1957).
— O. Pompeiano, and B. Waltman: Fast supraspinal control of mammalian spindles: extra- and intrafusal co-activation. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 147, 385–398 (1959a).
— The early discharge of mammalian muscle spindles at onset of contraction. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 147, 399–418 (1959b).
Haase, J., P. Meuser u. Ü. Tan: Die Konvergenz fusimotorischer α-Impulse auf de-efferentierte Flexorspindeln der Katze. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 289, 50–58 (1966).
—, u. H.-J. Schlegel: Einige funktionelle Merkmale von α-innervierten Extensor-und Flexorspindeln der Katze. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 287, 163–175 (1966).
Henatsch, H. D., u. F. J. Schulte: Einflüsse von Curare und Flaxedil auf die Muskelspindeln des Frosches. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 234, 247–263 (1958).
Hunt, C. C., and S. W. Kuffler: Further study of efferent small-nerve fibres to mammalian muscle spindles. Multiple spindle innervation and activity during contraction. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 113, 283–297 (1951).
Katz, B.: The efferent regulation of the muscle spindle in the frog. J. exp. Biol. 26, 201–217 (1949).
Rutledge, L. T., and J. Haase: Flexor muscle spindles and reflex firing of early discharging units. J. Neurophysiol. 24, 182–192 (1961).
Werner, G., and V. B. Mountcastle: Neural activity in mechano-receptive cutaneous afferents: stimulus-response relations, Weber functions, and information transmission. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 359–397 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrios, P., Haase, J., Heinrich, W. et al. Die Entladungen de-afferentierter Katzen-Flexormuskelspindeln mit fusimotorischer α- Innervation bei repetierender Reizung von Ventralwurzelfilamenten. Pflügers Archiv 290, 101–113 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00363688
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00363688