Summary
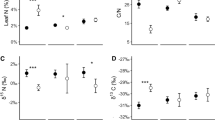
Under conditions where both plants had permanently low water status, the mistletoe, Amyema miquelii (Lehm. ex Miq.) Tiegh., had lower nitrogen contents in leaf tissue than its host, Eucalyptus behriana F. Muell. The parasite transpired less than its host which is consistent with the hypothesis that mistletoe transpiration acts as a nitrogen gathering mechanism. Nitrogen and phosphorus contents were generally low in both plants; they were positively correlated, and mistletoes reduced nutrient contents of infested hosts. The carbon discrimination ratio, δ13C (a measure of water-use efficiency) of each plant was within the range reported for other mistletoes and their hosts. Although it did not differ significantly between host and parasite it indicated lower water-use efficiency in the mistletoe. For the nitrogen content of host leaves the gradient within the pair, Δ(δ13C), is much lower compared to the correlation given by Ehleringer et al. (1985). It is concluded that at permanently low water status on nitrogen and phosphorus deficient soils a water-saving strategy accompanied with slow growth is more appropriate for both mistletoe and host.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beadle NCW (1981) The vegetation of Australia. Fischer, Stuttgart
Boland DJ, Brooker MIH, Chippendale GM, Hall N, Hyland BPM, Johnston RD, Kleinig DA, Turner JD (1984) Forest trees of Australia. Nelson, CSIRO, Melbourne
Craig H (1953) The geochemistry of stable carbon isotopes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 3: 53–92
Ehleringer JR, Schulze E-D (1985) Mineral concentrations in an autoparasitic Phoradendron californicum growing on a parasitic P. californium and its host, Cercidium floridum. Am J Bot 568–571
Ehleringer JR, Schulze E-D, Ziegler H, Lange OL, Farquhar GD, Cowan IR (1985) Xylem-tap** mistletoes: water or nutrient parasites? Science 227: 1479–1481
Ehleringer JR, Cook CS, Tieszen LL (1986a) Comparative water use and nitrogen relationships in a mistletoe and its host. Oecologia 68: 279–284
Ehleringer JR, Ullmann I, Lange OL, Farquhar GD, Cowan IR, Schulze E-D (1986b) Mistletoes: a hypothesis concerning morphological and chemical avoidance of herbivory. Oecologia 70: 234–237
Farquhar GD, O'Leary MH, Berry JA (1982) On the relationship between carbon isotope discrimination and the intercellular carbon dioxide concentration in leaves. Aust J Plant Physiol 9: 121–137
Glatzel G (1983) Mineral nutrition and water relations of hemiparasitic mistletoes: a question of partitioning. Experiments with Loranthus europaeus on Quercus petraea and Quercus robur. Oecologia 56: 193–201
Glatzel G, Balasubramaniam S (1987) Mineral nutrition of mistletoes: general concepts. In: Weber HC, Forstreuter W (eds) Parasitic flowering plants. Proceedings of the 4th ISPFP, Marburg, pp 263–276
Hefferman B (1985) A handbook of methods of inorganic chemical analysis for forest soils, foliage and water. CSIRO Division of Forest Research, Canberra
Hubick KT, Farquhar GD, Shorter R (1986) Correlation between water-use efficiency and carbon isotope discrimination in diverse peanut (Arachis) germplasm. Aust J Plant Physiol 13: 803–816
Küppers M, Neales TF, Küppers BIL, Swan AG, Myers BA (1987) Hydraulic flow characteristics in the lignotuberous mallee Eucalyptus behriana F. Muell. in the field. Plant Cell Env 10: 27–37
Küppers M, Küppers BIL, Neales TF, Swan AG (1992a) Leaf gas exchange characteristics, daily carbon and water balances of the host / mistletoe pair Eucalyptus behriana F. Muell, and Amyema miquelii (Lehm. ex Miq.) Tiegh. at permanently low plant water status in the field. Trees (in press)
Küppers M, Küppers BIL, Neales TF, Swan AG (1992b) Water relations, hydraulic conductivity and response to stem excision under water of the host / mistletoe pair Eucalyptus behriana F. Muell. and Amyema miquelii (Lehm. ex Miq.) Tiegh. at permanently low plant water status in the field. Trees (in press)
Lillivek HA (1970) The determination of total organic nitrogen. In: Joslyn MA (ed) Methods in food analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp 601–616
Marshall JD, Ehleringer JR (1990) Are xylem-tap** mistletoes partially heterotrophic? Oecologia 84: 244–248
Myers BA, Neales TF (1984) Seasonal changes in the water relations of Eucalyptus behriana F. Muell. and E. microcarpa (Maiden) Maiden. Aust J Bot 23: 495–510
Myers BA, Ashton DH, Osborne JA (1986) The ecology of the mallee outlier of Eucalyptus behriana F. Muell. near Melton, Victoria. Aust J Bot 34: 15–39
Osmond CB, Ziegler H, Stichler W, Trimborn P (1975) Carbon isotope discrimination in alpine succulent plants supposed to be capable of crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM). Oecologia 18: 209–217
Schulze E-D, Ehleringer JR (1984) The effect of nitrogen supply on growth and water-use efficiency of xylem tap** mistletoes. Planta 162: 268–275
Schulze E-D, Turner NC, Glatzel G (1984) Carbon, water and nutrient relations of two mistletoes and their hosts: a hypothesis. Plant Cell Env 7: 293–299
Schulze E-D, Lange OL, Ziegler H, Gebauer G (1991) Carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios of mistletoes growing on nitrogen and non-nitrogen fixing hosts and on CAM plants in the Namib desert confirm partial heterotrophy. Oecologia 88: 457–462
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Küppers, M. Carbon discrimination, water-use efficiency, nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition of the host / mistletoe pair Eucalyptus behriana F. Muell and Amyema miquelii (Lehm. ex Miq.) Tiegh. at permanently low plant water status in the field. Trees 7, 8–11 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225226
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225226