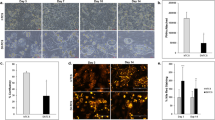
The known biodegradability of poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid] (PHB) in certain biological environments has lead to its proposed use as biodegradable, biocompatible polymer. Recently, a new, rapidly biodegradable blockcopolymer has been synthesized that contains crystalline domains of PHB blocks. During degradation of these polymers, the PHB-domains are transformed in a first step into small crystalline particles of short-chain PHB. Therefore, particles of short-chain poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid] (Mn≈2300) (PHB-P), as possible degradation products, are investigated here for their effects on the viability and activation of macrophages, fibroblasts, and co-cultures of rat Kupffer cells and rat hepatocytes. Results obtained in the present study indicate that phagocytosis of particles of short-chain poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid] at high concentrations (higher than 10 μg/ml) is dosedependent and associated with cell damage in macrophages but not in fibroblasts. At low concentrations, particles of PHB-P also failed to activate macrophages and are biocompatible. Besides the PHB phagocytosis by Kupffer cells, treatment of co-cultures of Kupffer cells and hepatocytes with 1 μg PHB/ml showed neither cytotoxic (lactate dehydrogenase activity) effects nor any change in albumin secretion by hepatocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. M. Aupnderson, Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2 (1993) 3: 33S.
J. M. Supchakenraad, J. A. Ouposterbaan, P. Nupiewenhuis, I. Mupolennaar, J. Ouplijslager, W. Pupotman, M. J. D. Eupenink and J. Fupeijen, Biomaterials 9 (1988) 116.
J. M. Aupnderson and K. M. Mupiller, Biomaterials 5 (1984) 5.
J. M. Pupapadimitriou and M. N. I. Wupalters, CRC Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 9 (1979) 211.
Y. Tupabata and Y. Iupkata, Adv. Polym. Sci. 94 (1990) 108.
G. Cupiardelli, B. Supaad, T. Hupirt, G. K. Uuphlschmid, P. Nupeuenschwander and U. W. Suputer, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. (in press).
B. Supaad, H. Tuphomas, H. P. Supchawalder, F. Wupaechter and P. Mupaier. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 126 (1994) 372.
B. Supaad, H. P. Supchawalder and P. Mupaier, In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 29A (1993) 32.
M. M. Bupradford, Anal. Biochem. 72 (1976) 248.
T. Eupspevik and J. Nupissen-Mupeyer, J. Immunol. Methods 95 (1986) 99.
A. H. Du**, C. F. Nupathan and D. J. Suptuehr, J. Immunol. 141 (1988) 2407.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saad, B., Ciardelli, G., Matter, S. et al. Cell response of cultured macrophages, fibroblasts, and co-cultures of Kupffer cells and hepatocytes to particles of short-chain poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid]. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 7, 56–61 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121191
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121191